Long non-coding RNAs as regulators of the endocrine system
- PMID: 25560704
- PMCID: PMC4376378
- DOI: 10.1038/nrendo.2014.229
Long non-coding RNAs as regulators of the endocrine system
Abstract
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a large and diverse group of RNAs that are often lineage-specific and that regulate multiple biological functions. Many are nuclear and are essential parts of ribonucleoprotein complexes that modify chromatin segments and establish active or repressive chromatin states; others are cytosolic and regulate the stability of mRNA or act as microRNA sponges. This Review summarizes the current knowledge of lncRNAs as regulators of the endocrine system, with a focus on the identification and mode of action of several endocrine-important lncRNAs. We highlight lncRNAs that have a role in the development and function of pancreatic β cells, white and brown adipose tissue, and other endocrine organs, and discuss the involvement of these molecules in endocrine dysfunction (for example, diabetes mellitus). We also address the associations of lncRNAs with nuclear receptors involved in major hormonal signalling pathways, such as estrogen and androgen receptors, and the relevance of these associations in certain endocrine cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
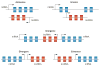
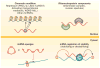

References
-
- Amaral PP, Dinger ME, Mercer TR, Mattick JS. The eukaryotic genome as an RNA machine. Science. 2008;319:1787–1789. - PubMed
-
- Kapranov P, et al. Large-scale transcriptional activity in chromosomes 21 and 22. Science. 2002;296:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Wahlestedt C. Natural antisense and noncoding RNA transcripts as potential drug targets. Drug Discov Today. 2006;11:503–508. - PubMed
-
- Kawai J, et al. Functional annotation of a full-length mouse cDNA collection. Nature. 2001;409:685–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

