The G-patch protein Spp2 couples the spliceosome-stimulated ATPase activity of the DEAH-box protein Prp2 to catalytic activation of the spliceosome
- PMID: 25561498
- PMCID: PMC4285774
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.253070.114
The G-patch protein Spp2 couples the spliceosome-stimulated ATPase activity of the DEAH-box protein Prp2 to catalytic activation of the spliceosome
Abstract
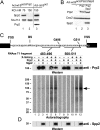
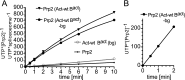
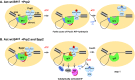
Structural rearrangement of the activated spliceosome (B(act)) to yield a catalytically active complex (B*) is mediated by the DEAH-box NTPase Prp2 in cooperation with the G-patch protein Spp2. However, how the energy of ATP hydrolysis by Prp2 is coupled to mechanical work and what role Spp2 plays in this process are unclear. Using a purified splicing system, we demonstrate that Spp2 is not required to recruit Prp2 to its bona fide binding site in the B(act) spliceosome. In the absence of Spp2, the B(act) spliceosome efficiently triggers Prp2's NTPase activity, but NTP hydrolysis is not coupled to ribonucleoprotein (RNP) rearrangements leading to catalytic activation of the spliceosome. Transformation of the B(act) to the B* spliceosome occurs only when Spp2 is present and is accompanied by dissociation of Prp2 and a reduction in its NTPase activity. In the absence of spliceosomes, Spp2 enhances Prp2's RNA-dependent ATPase activity without affecting its RNA affinity. Our data suggest that Spp2 plays a major role in coupling Prp2's ATPase activity to remodeling of the spliceosome into a catalytically active machine.
Keywords: ATP hydrolysis; DEAH-box helicase; G-patch protein; Prp2; Spp2; spliceosome activation.
© 2015 Warkocki et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mechanism of spliceosome remodeling by the ATPase/helicase Prp2 and its coactivator Spp2.Science. 2021 Jan 8;371(6525):eabe8863. doi: 10.1126/science.abe8863. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Science. 2021. PMID: 33243853
-
Structural analysis of the intrinsically disordered splicing factor Spp2 and its binding to the DEAH-box ATPase Prp2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Feb 11;117(6):2948-2956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1907960117. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 31974312 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between a G-patch protein and a spliceosomal DEXD/H-box ATPase that is critical for splicing.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Dec;24(23):10101-10. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.23.10101-10110.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15542821 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of spliceosomal DEAH-box ATPases.Biol Chem. 2023 Jul 17;404(8-9):851-866. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2023-0157. Print 2023 Jul 26. Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37441768 Review.
-
Splicing fidelity: DEAD/H-box ATPases as molecular clocks.RNA Biol. 2013 Jul;10(7):1073-9. doi: 10.4161/rna.25245. Epub 2013 Jun 3. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23770752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional analysis of Cwc24 ZF-domain in 5' splice site selection.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Nov 4;47(19):10327-10339. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz733. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31504764 Free PMC article.
-
The RES complex is required for efficient transformation of the precatalytic B spliceosome into an activated Bact complex.Genes Dev. 2017 Dec 1;31(23-24):2416-2429. doi: 10.1101/gad.308163.117. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 29330354 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the mechanism of the DEAH-box RNA helicase Prp43.Elife. 2017 Jan 16;6:e21510. doi: 10.7554/eLife.21510. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28092261 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of cis- and trans-regulatory mechanisms in the spliceosomal RNA helicase Brr2.Cell Cycle. 2017 Jan 2;16(1):100-112. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1255384. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 27880071 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the yeast spliceosomal postcatalytic P complex.Science. 2017 Dec 8;358(6368):1278-1283. doi: 10.1126/science.aar3462. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Science. 2017. PMID: 29146870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aravind L, Koonin EV. 1999. G-patch: a new conserved domain in eukaryotic RNA-processing proteins and type D retroviral polyproteins. Trends Biochem Sci 24: 342–344. - PubMed
-
- Burgess SM, Guthrie C. 1993. Beat the clock: paradigms for NTPases in the maintenance of biological fidelity. Trends Biochem Sci 18: 381–384. - PubMed
-
- Buttner K, Nehring S, Hopfner KP. 2007. Structural basis for DNA duplex separation by a superfamily-2 helicase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14: 647–652. - PubMed
-
- Cashel M, Lazzarini RA, Kalbacher B. 1969. An improved method for thin-layer chromatography of nucleotide mixtures containing 32P-labelled orthophosphate. J Chromatogr 40: 103–109. - PubMed
-
- Chan SP, Cheng SC. 2005. The Prp19-associated complex is required for specifying interactions of U5 and U6 with pre-mRNA during spliceosome activation. J Biol Chem 280: 31190–31199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
