Single cell-derived clonal analysis of human glioblastoma links functional and genomic heterogeneity
- PMID: 25561528
- PMCID: PMC4311802
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1320611111
Single cell-derived clonal analysis of human glioblastoma links functional and genomic heterogeneity
Abstract
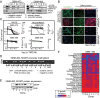
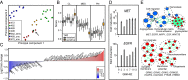
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a cancer comprised of morphologically, genetically, and phenotypically diverse cells. However, an understanding of the functional significance of intratumoral heterogeneity is lacking. We devised a method to isolate and functionally profile tumorigenic clones from patient glioblastoma samples. Individual clones demonstrated unique proliferation and differentiation abilities. Importantly, naïve patient tumors included clones that were temozolomide resistant, indicating that resistance to conventional GBM therapy can preexist in untreated tumors at a clonal level. Further, candidate therapies for resistant clones were detected with clone-specific drug screening. Genomic analyses revealed genes and pathways that associate with specific functional behavior of single clones. Our results suggest that functional clonal profiling used to identify tumorigenic and drug-resistant tumor clones will lead to the discovery of new GBM clone-specific treatment strategies.
Keywords: cancer; clonal heterogeneity; functional analysis; genomic analysis; glioblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

