Signature of consciousness in the dynamics of resting-state brain activity
- PMID: 25561541
- PMCID: PMC4311826
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1418031112
Signature of consciousness in the dynamics of resting-state brain activity
Erratum in
-
Correction for Barttfeld et al., Signature of consciousness in the dynamics of resting-state brain activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 15;112(37):E5219-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515029112. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26324930 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
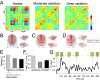
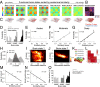
At rest, the brain is traversed by spontaneous functional connectivity patterns. Two hypotheses have been proposed for their origins: they may reflect a continuous stream of ongoing cognitive processes as well as random fluctuations shaped by a fixed anatomical connectivity matrix. Here we show that both sources contribute to the shaping of resting-state networks, yet with distinct contributions during consciousness and anesthesia. We measured dynamical functional connectivity with functional MRI during the resting state in awake and anesthetized monkeys. Under anesthesia, the more frequent functional connectivity patterns inherit the structure of anatomical connectivity, exhibit fewer small-world properties, and lack negative correlations. Conversely, wakefulness is characterized by the sequential exploration of a richer repertoire of functional configurations, often dissimilar to anatomical structure, and comprising positive and negative correlations among brain regions. These results reconcile theories of consciousness with observations of long-range correlation in the anesthetized brain and show that a rich functional dynamics might constitute a signature of consciousness, with potential clinical implications for the detection of awareness in anesthesia and brain-lesioned patients.
Keywords: anesthesia; consciousness; dynamics; functional connectivity; structural connectivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sporns O, Zwi JD. The small world of the cerebral cortex. Neuroinformatics. 2004;2(2):145–162. - PubMed
-
- Spreng RN, Mar RA, Kim AS. The common neural basis of autobiographical memory, prospection, navigation, theory of mind, and the default mode: A quantitative meta-analysis. J Cogn Neurosci. 2009;21(3):489–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

