K-Ras4A splice variant is widely expressed in cancer and uses a hybrid membrane-targeting motif
- PMID: 25561545
- PMCID: PMC4311840
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1412811112
K-Ras4A splice variant is widely expressed in cancer and uses a hybrid membrane-targeting motif
Abstract
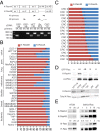
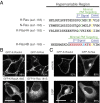
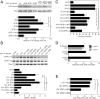
The two products of the KRAS locus, K-Ras4A and K-Ras4B, are encoded by alternative fourth exons and therefore, possess distinct membrane-targeting sequences. The common activating mutations occur in exons 1 or 2 and therefore, render both splice variants oncogenic. K-Ras4A has been understudied, because it has been considered a minor splice variant. By priming off of the splice junction, we developed a quantitative RT-PCR assay for K-Ras4A and K-Ras4B message capable of measuring absolute amounts of the two transcripts. We found that K-Ras4A was widely expressed in 30 of 30 human cancer cell lines and amounts equal to K-Ras4B in 17 human colorectal tumors. Using splice variant-specific antibodies, we detected K-Ras4A protein in several tumor cell lines at a level equal to or greater than that of K-Ras4B. In addition to the CAAX motif, the C terminus of K-Ras4A contains a site of palmitoylation as well as a bipartite polybasic region. Although both were required for maximal efficiency, each of these could independently deliver K-Ras4A to the plasma membrane. Thus, among four Ras proteins, K-Ras4A is unique in possessing a dual membrane-targeting motif. We also found that, unlike K-Ras4B, K-Ras4A does not bind to the cytosolic chaperone δ-subunit of cGMP phosphodiesterase type 6 (PDE6δ). We conclude that efforts to develop anti-K-Ras drugs that interfere with membrane trafficking will have to take into account the distinct modes of targeting of the two K-Ras splice variants.
Keywords: K-Ras; Ras; alternate splicing; oncogene; palmitoylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Willumsen BM, Christensen A, Hubbert NL, Papageorge AG, Lowy DR. The p21 ras C-terminus is required for transformation and membrane association. Nature. 1984;310(5978):583–586. - PubMed
-
- Wright LP, Philips MR. Thematic review series: Lipid posttranslational modifications. CAAX modification and membrane targeting of Ras. J Lipid Res. 2006;47(5):883–891. - PubMed
-
- Choy E, et al. Endomembrane trafficking of ras: The CAAX motif targets proteins to the ER and Golgi. Cell. 1999;98(1):69–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R21 CA161494/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA178017/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA116034/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM055279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA042978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116034/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA178017/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA167910/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30CA167910/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA163489/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM055279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA161494/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA042978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

