2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced chronic colitis with fibrosis and modulation of TGF-β1 signaling
- PMID: 25561788
- PMCID: PMC4277958
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18207
2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced chronic colitis with fibrosis and modulation of TGF-β1 signaling
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether targeting proteasome might reverse intestinal fibrosis in rats.
Methods: Chronic colitis was induced in rats by repeated administration of increasing dose of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS, 15, 30, 45, 60, 60, 60 mg) by rectal injection for 6 wk (from day 0 to day 35), while control rats received the vehicle. TNBS + bortezomib (BTZ) rats received intraperitoneal injections of BTZ twice weekly (from day 37 to day 44) at a dose of 25 mg/kg, whereas the control and TNBS groups received the same amount of the vehicle. Histologic scoring of inflammation and fibrosis was performed. Colonic production of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β was measured by ELISA. Colon fibrosis-related proteins such as phospho-p38, phospho-SMAD2/3, Akt and peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ) were studied by western blot. Expression of the tight junction proteins, occludin and claudin-1, were assessed by Western blot. Colon proteasome activities (chymotrypsin-like and trypsin-like activities) were assessed.
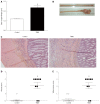
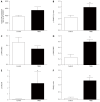
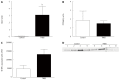
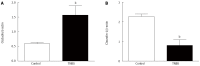
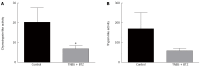
Results: TNBS-treated rats had a higher colon weight/length ratio compared to control rats (P < 0.01). Furthermore, fibrosis and inflammation scores were higher in TNBS-treated rats compared to control rats (P < 0.01 for both). Colonic production of TGF-β production tended to be higher in TNBS-treated rats (P < 0.06). Fibrosis-related proteins such as phospho-p38, phospho-SMAD2/3, and PPARγ were significantly higher in TNBS-treated rats compared to control rats (all P < 0.05). TNBS rats had a higher expression of Akt compared to control rats (P < 0.01). Tight junction proteins were modified by repeated TNBS challenge: colon occludin expression rose significantly (P < 0.01), whereas claudin-1 expression fell (P < 0.01). Bortezomib inhibition significantly decreased chymotrypsin-like activity (P < 0.05), but had no significant effect on trypsin-like activity (P > 0.05). In contrast, bortezomib had no effect on other studied parameters such as fibrosis score, TGF-β signaling, or tight junction expression (P > 0.05 for all).
Conclusion: Rats with TNBS-induced chronic colitis exhibited colon fibrosis associated with higher TGF-β signaling. Proteasome inhibition by bortezomib had no effect on fibrosis in our experimental conditions.
Keywords: Bortezomib; Colitis; Fibrosis; Proteasome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevention of colonic fibrosis by Boswellia and Scutellaria extracts in rats with colitis induced by 2,4,5-trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid.Eur J Clin Invest. 2008 Jun;38(6):410-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2008.01955.x. Eur J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18489401
-
IL-13 signaling via IL-13R alpha2 induces major downstream fibrogenic factors mediating fibrosis in chronic TNBS colitis.Gastroenterology. 2008 Dec;135(6):2003-13, 2013.e1-7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.055. Epub 2008 Sep 11. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18938165
-
A polymeric diet rich in transforming growth factor beta 2 does not reduce inflammation in chronic 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis in pre-pubertal rats.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Dec 10;20(1):416. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01574-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33302890 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasomal regulation of pulmonary fibrosis.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2010 Feb;7(1):77-83. doi: 10.1513/pats.200906-055JS. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2010. PMID: 20160152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokines mediating the induction of chronic colitis and colitis-associated fibrosis.Mucosal Immunol. 2008 Nov;1 Suppl 1(0 1):S24-7. doi: 10.1038/mi.2008.41. Mucosal Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19079223 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Authors' Reply.Am J Pathol. 2024 Jun;194(6):1156-1157. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2024.03.007. Am J Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38749611 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sishen Pill Maintained Colonic Mucosal Barrier Integrity to Treat Ulcerative Colitis via Rho/ROCK Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Dec 9;2021:5536679. doi: 10.1155/2021/5536679. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34925530 Free PMC article.
-
Herbs-Partitioned Moxibustion Combined with Acupuncture Inhibits TGF-β1-Smad-Snail-Induced Intestinal Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Crohn's Disease Model Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 May 30;2019:8320250. doi: 10.1155/2019/8320250. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31275422 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Claudins in the Pathogenesis of Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Experimental Colitis: The Effects of Nobiletin.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 4;14(9):1122. doi: 10.3390/biom14091122. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334888 Free PMC article.
-
Rectal roflumilast improves trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced chronic colitis in rats.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022 Feb 28;55:e11877. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2021e11877. eCollection 2022. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 35239781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andoh A, Tsujikawa T, Ishizuka I, Araki Y, Sasaki M, Koyama S, Fujiyama Y. N-3 fatty acid-rich diet prevents early response of interleukin-6 elevation in trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced enteritis. Int J Mol Med. 2003;12:721–725. - PubMed
-
- Charpentier C, Marion-Letellier R, Savoye G, Nicol L, Mulder P, Aziz M, Vera P, Déchelotte P, Savoye-Collet C. Magnetic resonance colonography in rats with TNBS-induced colitis: a feasibility and validation study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18:1940–1949. - PubMed
-
- Hassan A, Ibrahim A, Mbodji K, Coëffier M, Ziegler F, Bounoure F, Chardigny JM, Skiba M, Savoye G, Déchelotte P, et al. An α-linolenic acid-rich formula reduces oxidative stress and inflammation by regulating NF-κB in rats with TNBS-induced colitis. J Nutr. 2010;140:1714–1721. - PubMed
-
- Mbodji K, Charpentier C, Guérin C, Querec C, Bole-Feysot C, Aziz M, Savoye G, Déchelotte P, Marion-Letellier R. Adjunct therapy of n-3 fatty acids to 5-ASA ameliorates inflammatory score and decreases NF-κB in rats with TNBS-induced colitis. J Nutr Biochem. 2013;24:700–705. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

