Novel patchouli alcohol ternary solid dispersion pellets prepared by poloxamers
- PMID: 25561908
- PMCID: PMC4277615
Novel patchouli alcohol ternary solid dispersion pellets prepared by poloxamers
Abstract
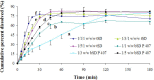
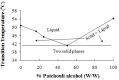
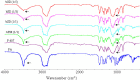
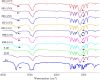
The present study investigates the possibility of using poloxamers as solubility and dissolution rate enhancing agents of poorly water soluble bioactive constituent patchouli alcohol (PA) that can be used for the preparation of immediate release pellets formulation. Two commercially available grades poloxamer 188 (P 188) and poloxamer 407 (P 407) were selected, and solid dispersions (SDs) containing different weight ratio of PA and poloxamers, and the combination of P 188 and P 407 as dispersing carriers of ternary solid dispersions (tSDs) were prepared by a low temperature melting method and solidified rapidly by dropping into the 10-15 °C condensing agent atoleine. Both PA/P 188 and PA/P 407 binary solid dispersions (bSDs) could remarkably promote the dissolution rate of PA, increasing approximately 16 times in bSDs with poloxamers in comparison with pure PA within 180 min. P188 contributed to a faster dissolution rate than P 407, however, P 407 had a better solubility. It is interesting to note that the incorporation of P 188 in PA/P 407 bSD pellets could strongly enhance the dissolution rate of PA. DSC and FTIR were used to explore the characteristics of PA-SD pellets. The enhancement of dissolution from the SDs may be attributed partly to the reduction in particle size in PA crystalline due to the formation of eutectic system with poloxamers. Moreover, a simple, accurate in-vitro dissolution test method for volatility drug was established, and the process of PA-SD pellets preparation was simple, rapid, cost effective, uncomplicated and potentially scalable.
Keywords: Closed in-vitro dissolution test method; Eutectic mixtures; Patchouli alcohol; Poloxamers; Ternary solid dispersion pellets.
Figures








References
-
- Lai XP, Su ZR, Chen JN, Li YC, He JJ. Application of patchouli alcohol in preparation of anti-Helicobacter pylori infection medicine. State Intellectual Property of P. R. C. China patent; 2012.
-
- Li YC, Xian YF, Ip SP, Su ZR, Su JY, He JJ, Xie QF, Lai XP, Lin ZX. Anti-inflammatory activity of patchouli alcohol isolated from Pogostemonis Herba in animal models. Fitoterapia . 2011;82:1295–1301. - PubMed
-
- Li YC, Peng SZ, Chen HM, Zhang FX, Xu PP, Xie JH, He JJ, Chen JN, Lai XP, Su ZR. Oral administration of patchouli alcohol isolated from Pogostemonis Herba augments protection against influenza viral infection in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012;12:294–301. - PubMed
-
- Huang XW, Bai L, Xu FH, Wu YJ. Inhibitory activities of patchouli alcohol on neurotoxicity of β-amyloid peptide. Jie Fang Jun Yi Xue Za Zhi . 2008;24:338–340.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
