Variations in Intraplatelet Phospho-VASP Expression Due to Pre-analytical Sample Preparations, Illustration of a Quality Control Issue in Platelet Pharmacology
- PMID: 25561938
- PMCID: PMC4277645
Variations in Intraplatelet Phospho-VASP Expression Due to Pre-analytical Sample Preparations, Illustration of a Quality Control Issue in Platelet Pharmacology
Abstract
Intraplatelet vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) analysis is a commonly used laboratory approach for monitoring of the anti-platelet therapy with adenosine diphosphate (ADP) receptor blocking agents; however, it's testing in clinical laboratory needs a high level of experience and proficiency. The ability to recognize how the pre-analytical variations can change the results would be helpful for the interpretation of data from intraplatelet VASP analysis. The aim of this study was to describe the possible differences of intraplatelet phospho-VASP expression between washed and platelet rich plasma (PRP) samples, both at baseline levels and following experimentally induction of VASP phosphorylation. PRP and washed platelet samples were treated with different inducers of VASP phosphorylation, including forskolin (10 µM), prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) (50 nM) and sodium nitro-prusside (SNP) (100 µM). Untreated PRP and washed platelet samples were also included in study as baseline controls. After labeling of platelets with either anti P-Serine(157)-VASP or anti P-Serine(239)-VASP, the samples were subjected to flow cytometric analysis to monitor the levels of intraplatelet phospho-VASP expression. Washed platelet samples tend to show increased expression of intraplatelet P-Serine(157)-VASP at baseline state and also more expression of P-Serine(157)-VASP and P-Serine(239)-VASP in response to forskolin and SNP, compared with PRP samples. Though, reduced levels of PGE1-induced VASP phosphorylation at both residues were detected for washed platelets. In this study we have provided some background information required for performing of intraplatelet VASP analysis on differently handled platelet samples and interpretation of the obtained results.
Keywords: Flow cytometry; PRP; Platelet; Pre-analytical variation; Quality control; VASP.
Figures
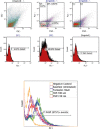
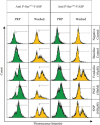
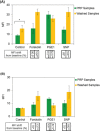
Similar articles
-
[Platelet responsiveness to clopidogrel in patients with coronary syndrome. Comparison of platelet aggregation induced by ADP and flow cytometric analysis of intraplatelet VASP phosphorylation].Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2007 Jan;56(1):21-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ancard.2006.11.005. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2007. PMID: 17343035 French.
-
Comparison of VASP-phosphorylation assay to light-transmission aggregometry in assessing inhibition of the platelet ADP P2Y12 receptor.Thromb Haemost. 2006 Dec;96(6):767-73. Thromb Haemost. 2006. PMID: 17139371
-
Concentration and regulation of cyclic nucleotides, cyclic-nucleotide-dependent protein kinases and one of their major substrates in human platelets. Estimating the rate of cAMP-regulated and cGMP-regulated protein phosphorylation in intact cells.Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 15;205(2):471-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16803.x. Eur J Biochem. 1992. PMID: 1315268
-
Decreased VASP phosphorylation in platelets of male and female smokers of young age.Platelets. 2010;21(8):596-603. doi: 10.3109/09537104.2010.505674. Epub 2010 Sep 7. Platelets. 2010. PMID: 20822337
-
Phosphorylation of focal adhesion vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein at Ser157 in intact human platelets correlates with fibrinogen receptor inhibition.Eur J Biochem. 1994 Oct 1;225(1):21-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.00021.x. Eur J Biochem. 1994. PMID: 7925440
Cited by
-
Platelet Activation and Clopidogrel Effects on ADP-Induced Platelet Activation in Cats with or without the A31P Mutation in MYBPC3.J Vet Intern Med. 2016 Sep;30(5):1619-1629. doi: 10.1111/jvim.14568. Epub 2016 Sep 12. J Vet Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 27615120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thijs T, Nuyttens BP, Deckmyn H, Broos K. Platelet physiology and antiplatelet agents. Clin. Chem. Laborator. Med. 2010;48:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Aszodi A, Pfeifer A, Ahmad M, Glauner M, Zhou XH, Ny L, Andersson KE, Kehrel B, Offermanns S, Fässler R. The vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) is involved in cGMP- and cAMP-mediated inhibition of agonist-induced platelet aggregation, but is dispensable for smooth muscle function. EMBO J. 1999;18:37–48. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
