Antisense therapy in neurology
- PMID: 25562650
- PMCID: PMC4251390
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm3030144
Antisense therapy in neurology
Abstract
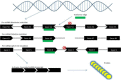
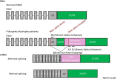
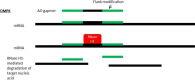
Antisense therapy is an approach to fighting diseases using short DNA-like molecules called antisense oligonucleotides. Recently, antisense therapy has emerged as an exciting and promising strategy for the treatment of various neurodegenerative and neuromuscular disorders. Previous and ongoing pre-clinical and clinical trials have provided encouraging early results. Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), Huntington's disease (HD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy (FCMD), dysferlinopathy (including limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2B; LGMD2B, Miyoshi myopathy; MM, and distal myopathy with anterior tibial onset; DMAT), and myotonic dystrophy (DM) are all reported to be promising targets for antisense therapy. This paper focuses on the current progress of antisense therapies in neurology.
Figures

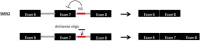
References
-
- Bennett C.F., Condon T.P., Grimm S., Chan H., Chiang M.Y. Inhibition of endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression with antisense oligonucleotides. J. Immunol. 1994;152:3530–3540. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

