The effect of soybean isoflavone on the dysregulation of NMDA receptor signaling pathway induced by β-amyloid peptides 1-42 in rats
- PMID: 25563203
- PMCID: PMC11488059
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-014-0151-9
The effect of soybean isoflavone on the dysregulation of NMDA receptor signaling pathway induced by β-amyloid peptides 1-42 in rats
Abstract
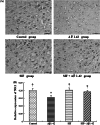
Synaptic damage is the key factor of cognitive impairment. The purpose of this study was to understand the effect of soybean isoflavone (SIF) on synaptic damage induced by β-amyloid peptide 1-42 (Aβ1-42) in rats. Adult male Wistar rats were randomly divided into control, Aβ1-42, SIF, and SIF + Aβ1-42 (SIF pretreatment) groups according to body weight. SIF was treated orally by gavage in SIF and SIF + Aβ1-42 groups. After 14 days pretreatment with SIF or vehicle, Aβ1-42 was injected into the lateral cerebral ventricle of rats in Aβ1-42 and SIF + Aβ1-42 groups using miniosmotic pump. The level of Aβ1-42 and the expression of N-methyl-D-aspartic-acid receptor (NMDAR) were observed by immunohistochemistry. Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction was used to detect the mRNA levels of NMDAR, calmodulin (CaM), calcium/CaM-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB), and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). The results showed that Aβ1-42 down-regulated mRNA and protein expression of the NR1 and NR2B subunits of NMDAR, SIF pretreatment could reverse these changes. The mRNA expression of CaM, CaMKII, CREB, and BDNF were down-regulated by Aβ1-42, but they were all regulated by SIF pretreatment. These results suggest that SIF pretreatment could antagonize the neuron damage in rats induced by Aβ1-42, and its mechanism might be associated with the NMDA receptor and CaM/CaMKII/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway, which are the synaptic plasticity-related molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this study.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Soybean isoflavone ameliorates β-amyloid 1-42-induced learning and memory deficit in rats by protecting synaptic structure and function.Synapse. 2013 Dec;67(12):856-64. doi: 10.1002/syn.21692. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Synapse. 2013. PMID: 23766238
-
Antagonizing effects of soybean isoflavones on β-amyloid peptide-induced oxidative damage in neuron mitochondria of rats.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012 Oct;111(4):248-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2012.00900.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22551092
-
Soy isoflavone attenuates brain mitochondrial oxidative stress induced by β-amyloid peptides 1-42 injection in lateral cerebral ventricle.J Neurosci Res. 2013 Apr;91(4):562-7. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23163. Epub 2012 Dec 13. J Neurosci Res. 2013. PMID: 23239252
-
Pattern recognition receptors involved in the inflammatory attenuating effects of soybean isoflavone in β-amyloid peptides 1-42 treated rats.Neurosci Lett. 2012 Jan 11;506(2):266-70. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.11.020. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Neurosci Lett. 2012. PMID: 22133809
-
Soybean isoflavone alleviates β-amyloid 1-42 induced inflammatory response to improve learning and memory ability by down regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 expression and nuclear factor-κB activity in rats.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2011 Aug;29(5):537-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2011.04.002. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21515354
Cited by
-
Amyloid-β(25-35) Modulates the Expression of GirK and KCNQ Channel Genes in the Hippocampus.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 28;10(7):e0134385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134385. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26218288 Free PMC article.
-
The Protective Effects of Zeaxanthin on Amyloid-β Peptide 1-42-Induced Impairment of Learning and Memory Ability in Rats.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jun 23;16:912896. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.912896. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35813593 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative transcriptomic and proteomic analysis reveals that SERPING1 inhibits neuronal proliferation via the CaMKII-CREB-BDNF pathway in schizophrenia.World J Psychiatry. 2025 Feb 19;15(2):100214. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i2.100214. eCollection 2025 Feb 19. World J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39974493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ding BJ, Ma WW, He LL, Zhou X, Yuan LH, Yu HL, Feng JF, Xiao R (2011) Soybean isoflavone alleviates beta-amyloid 1-42 induced inflammatory response to improve learning and memory ability by down regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 expression and nuclear factor-kappaB activity in rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 29(5):537–542 - PubMed
-
- Ding J, Xi YD, Zhang DD, Zhao X, Liu JM, Li CQ, Han J, Xiao R (2013) Soybean isoflavone ameliorates beta-amyloid 1-42-induced learning and memory deficit in rats by protecting synaptic structure and function. Synapse 67(12):856–864 - PubMed
-
- Diniz BS, Teixeira AL (2011) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and Alzheimer’s disease: physiopathology and beyond. Neuromolecular Med 13(4):217–222 - PubMed
-
- Gouras GK, Almeida CG, Takahashi RH (2005) Intraneuronal Abeta accumulation and origin of plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 26(9):1235–1244 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

