Xingshentongqiao decoction mediates proliferation, apoptosis, orexin-A receptor and orexin-B receptor messenger ribonucleic acid expression and represses mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
- PMID: 25563321
- PMCID: PMC4837828
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.147826
Xingshentongqiao decoction mediates proliferation, apoptosis, orexin-A receptor and orexin-B receptor messenger ribonucleic acid expression and represses mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
Erratum in
-
Xingshentongqiao Decoction Mediates Proliferation, Apoptosis, Orexin-A Receptor and Orexin-B Receptor Messenger Ribonucleic Acid Expression and Represses Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling: Corrigendum.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015 Feb 5;128(3):426. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.150129. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015. PMID: 25635451 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
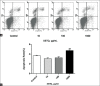
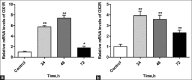
Background: Hypocretin (HCRT) signaling plays an important role in the pathogenesis of narcolepsy and can be significantly influenced by Chinese herbal therapy. Our previous study showed that xingshentongqiao decoction (XSTQ) is clinically effective for the treatment of narcolepsy. To determine whether XSTQ improves narcolepsy by modulating HCRT signaling, we investigated its effects on SH-SY5Y cell proliferation, apoptosis, and HCRT receptor 1/2 (orexin receptor 1 [OX1R] and orexin receptor 2 [OX2R]) expression. The signaling pathways involved in these processes were also assessed.
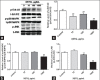
Methods: The effects of XSTQ on proliferation and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells were assessed using cell counting kit-8 and annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate assays. OX1R and OX2R expression was assessed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. Western blotting for mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway activation was performed to further assess the signaling mechanism of XSTQ.
Results: XSTQ reduced the proliferation and induced apoptosis of SH-SY5Y cells. This effect was accompanied by the upregulation of OX1R and OX2R expression and the reduced phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk) 1/2, p38 MAPK and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK).
Conclusions: XSTQ inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. XSTQ also promotes OX1R and OX2R expression. These effects are associated with the repression of the Erk1/2, p38 MAPK, and JNK signaling pathways. These results define a molecular mechanism for XSTQ in regulating HCRT and MAPK activation, which may explain its ability to treat narcolepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The signalling profile of recombinant human orexin-2 receptor.Cell Signal. 2008 Sep;20(9):1651-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.05.010. Epub 2008 May 27. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 18599270
-
Danshen-Gegen decoction exerts proliferative effect on rat cardiac myoblasts H9c2 via MAPK and insulin pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Oct 31;138(1):60-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.027. Epub 2011 Sep 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21907783
-
Effects of orexin A on GLUT4 expression and lipid content via MAPK signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Nov;138:376-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.07.005. Epub 2013 Jul 29. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23907013
-
Orexin in sleep, addiction and more: is the perfect insomnia drug at hand?Neuropeptides. 2013 Dec;47(6):477-88. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2013.10.009. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Neuropeptides. 2013. PMID: 24215799 Review.
-
Orexin receptors: multi-functional therapeutic targets for sleeping disorders, eating disorders, drug addiction, cancers and other physiological disorders.Cell Signal. 2013 Dec;25(12):2413-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.07.025. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23917208 Review.
Cited by
-
Xingshentongqiao Decoction Mediates Proliferation, Apoptosis, Orexin-A Receptor and Orexin-B Receptor Messenger Ribonucleic Acid Expression and Represses Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling: Corrigendum.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015 Feb 5;128(3):426. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.150129. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015. PMID: 25635451 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: A family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell. 1998;92:573–85. - PubMed
-
- Sakurai T. Roles of orexins and orexin receptors in central regulation of feeding behavior and energy homeostasis. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2006;5:313–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

