Cytokines, IBD, and colitis-associated cancer
- PMID: 25563695
- PMCID: PMC4481731
- DOI: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000236
Cytokines, IBD, and colitis-associated cancer
Abstract
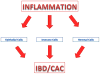
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) are debilitating conditions that result in intestinal damage due to chronic inflammation. In addition, the perpetual state of inflammation predisposes individuals to the development of colitis-associated cancer. Because of the immense immune cell infiltration into colon, cytokines produced by immune cells are major players in the initiation and progression of IBD and colitis-associated cancer. In this review, we will explore the functions of many key cytokines and their roles in IBD and colitis-associated cancer, as well as their influences on the immune system and stromal cells. Finally, we will briefly discuss current therapies and current clinical trials targeting cytokines in IBD.
Figures
References
-
- Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Crohn's disease. Lancet. 2012;380:1590–605. - PubMed
-
- Danese S, Fiocchi C. Ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1713–25. - PubMed
-
- Neurath MF. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:329–42. - PubMed
-
- Munkholm P. Review article: the incidence and prevalence of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;18(Suppl 2):1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

