Shear stress modulates endothelial KLF2 through activation of P2X4
- PMID: 25563726
- PMCID: PMC4336305
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-014-9442-3
Shear stress modulates endothelial KLF2 through activation of P2X4
Abstract
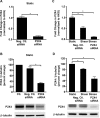
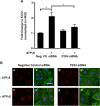
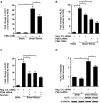
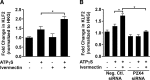
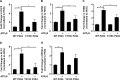
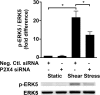
Vascular endothelial cells that are in direct contact with blood flow are exposed to fluid shear stress and regulate vascular homeostasis. Studies report endothelial cells to release ATP in response to shear stress that in turn modulates cellular functions via P2 receptors with P2X4 mediating shear stress-induced calcium signaling and vasodilation. A recent study shows that a loss-of-function polymorphism in the human P2X4 resulting in a Tyr315>Cys variant is associated with increased pulse pressure and impaired endothelial vasodilation. Although the importance of shear stress-induced Krüppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) expression in atheroprotection is well studied, whether ATP regulates KLF2 remains unanswered and is the objective of this study. Using an in vitro model, we show that in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), apyrase decreased shear stress-induced KLF2, KLF4, and NOS3 expression but not that of NFE2L2. Exposure of HUVECs either to shear stress or ATPγS under static conditions increased KLF2 in a P2X4-dependent manner as was evident with both the receptor antagonist and siRNA knockdown. Furthermore, transient transfection of static cultures of human endothelial cells with the Tyr315>Cys mutant P2X4 construct blocked ATP-induced KLF2 expression. Also, P2X4 mediated the shear stress-induced phosphorylation of extracellular regulated kinase-5, a known regulator of KLF2. This study demonstrates a major physiological finding that the shear-induced effects on endothelial KLF2 axis are in part dependent on ATP release and P2X4, a previously unidentified mechanism.
Figures
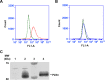
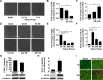
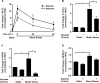
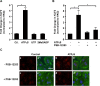
Similar articles
-
P2Y2 receptor modulates shear stress-induced cell alignment and actin stress fibers in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Feb;74(4):731-746. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2365-0. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27652381 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin counteracts high glucose-induced Krüppel-like factor 2 suppression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Postgrad Med. 2015 Jun;127(5):446-54. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2015.1039451. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Postgrad Med. 2015. PMID: 25927862
-
Laminar shear stress inhibits endothelial cell metabolism via KLF2-mediated repression of PFKFB3.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Jan;35(1):137-45. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304277. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25359860
-
[Blood flow sensing mechanism via calcium signaling in vascular endothelium].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010 Nov;130(11):1407-11. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.130.1407. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 21048396 Review. Japanese.
-
Role of Krüppel-like factor-2 in kidney disease.Nephrology (Carlton). 2018 Oct;23 Suppl 4:53-56. doi: 10.1111/nep.13456. Nephrology (Carlton). 2018. PMID: 30298668 Review.
Cited by
-
Purinoceptor: a novel target for hypertension.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):185-197. doi: 10.1007/s11302-022-09852-8. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 35181831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benfotiamine, a Lipid-Soluble Analog of Vitamin B1, Improves the Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Function in Blunt Snout Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) Fed High-Carbohydrate Diets by Promoting the AMPK/PGC-1β/NRF-1 Axis.Front Physiol. 2018 Sep 3;9:1079. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01079. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30233383 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y2 receptor modulates shear stress-induced cell alignment and actin stress fibers in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Feb;74(4):731-746. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2365-0. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27652381 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic Regulation of Endothelial Barrier Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 26;22(3):1207. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031207. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33530557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of silibinin on hepatic warm ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat model.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Jul;22(7):789-796. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.34967.8313. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 32373301 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

