Oxytocin receptor gene methylation: converging multilevel evidence for a role in social anxiety
- PMID: 25563749
- PMCID: PMC4397412
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2015.2
Oxytocin receptor gene methylation: converging multilevel evidence for a role in social anxiety
Abstract
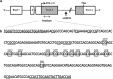
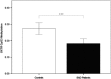
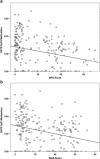
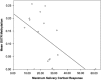
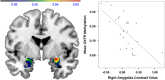
Social anxiety disorder (SAD) is a commonly occurring and highly disabling disorder. The neuropeptide oxytocin and its receptor (OXTR) have been implicated in social cognition and behavior. This study-for the first time applying a multilevel epigenetic approach-investigates the role of OXTR gene methylation in categorical, dimensional, and intermediate neuroendocrinological/neural network phenotypes of social anxiety. A total of 110 unmedicated patients with SAD and matched 110 controls were analyzed for OXTR methylation by direct sequencing of sodium bisulfite-converted DNA extracted from whole blood. Furthermore, OXTR methylation was investigated regarding SAD-related traits (Social Phobia Scale (SPS) and Social Interaction Anxiety Scale (SIAS)), salivary cortisol response during the Trier social stress test (TSST), and amygdala responsiveness to social phobia related verbal stimuli using fMRI. Significantly decreased OXTR methylation particularly at CpG Chr3: 8 809 437 was associated with (1) the categorical phenotype of SAD (p<0.001, Cohen's d=0.535), (2) increased SPS and SIAS scores (p<0.001), (3) increased cortisol response to the TSST (p=0.02), and (4) increased amygdala responsiveness during social phobia-related word processing (right: p(corr)<0.001; left: p(corr)=0.005). Assuming that decreased OXTR methylation confers increased OXTR expression, the present finding may reflect a compensatory upregulation for pathologically reduced oxytocin levels or a causally relevant increased OXTR activation in SAD and related traits. OXTR methylation patterns might thus serve as peripheral surrogates of oxytocin tone and aid in establishing accessible biomarkers of SAD risk allowing for indicated preventive interventions and personalized treatment approaches targeting the oxytocin system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxytocin and Anxiety Disorders.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;35:467-498. doi: 10.1007/7854_2017_25. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28812274 Review.
-
Oxytocin receptor gene methylation in male and female PTSD patients and trauma-exposed controls.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019 Jan;29(1):147-155. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30415783
-
Reduced DNA Methylation of the Oxytocin Receptor Gene Is Associated With Anhedonia-Asociality in Women With Recent-Onset Schizophrenia and Ultra-high Risk for Psychosis.Schizophr Bull. 2019 Oct 24;45(6):1279-1290. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbz016. Schizophr Bull. 2019. PMID: 31220321 Free PMC article.
-
The role of oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) DNA methylation (DNAm) in human social and emotional functioning: a systematic narrative review.BMC Psychiatry. 2018 May 29;18(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1740-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29843655 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modification of the oxytocin receptor gene influences the perception of anger and fear in the human brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Mar 17;112(11):3308-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1422096112. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25675509 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Natural variation in maternal care and cross-tissue patterns of oxytocin receptor gene methylation in rats.Horm Behav. 2016 Jan;77:42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.05.022. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Horm Behav. 2016. PMID: 26122287 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of 5-HTT variation, childhood trauma and self-efficacy on anxiety traits: a gene-environment-coping interaction study.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2016 Aug;123(8):895-904. doi: 10.1007/s00702-016-1564-z. Epub 2016 May 4. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2016. PMID: 27145764
-
OXTR polymorphisms associated with severity and treatment responses of schizophrenia.Schizophrenia (Heidelb). 2024 Jan 6;10(1):7. doi: 10.1038/s41537-023-00413-5. Schizophrenia (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38184684 Free PMC article.
-
Hypermethylation of the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) in obsessive-compulsive disorder: further evidence for a biomarker of disease and treatment response.Epigenetics. 2022 Jun;17(6):642-652. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2021.1943864. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 34269138 Free PMC article.
-
Mild internet use is associated with epigenetic alterations of key neurotransmission genes in salivary DNA of young university students.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 14;13(1):22192. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49492-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38092954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA; 2013.
-
- Baayen R, Piepenbrock R, Gulikers L. The CELEX lexical database (Release 2) Linguistic Data Consortium, University of Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania, PA; 1995.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

