Reverse zoonosis of influenza to swine: new perspectives on the human-animal interface
- PMID: 25564096
- PMCID: PMC4348213
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.12.002
Reverse zoonosis of influenza to swine: new perspectives on the human-animal interface
Abstract
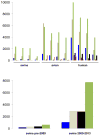
The origins of the 2009 influenza A (H1N1) pandemic in swine are unknown, highlighting gaps in our understanding of influenza A virus (IAV) ecology and evolution. We review how recently strengthened influenza virus surveillance in pigs has revealed that influenza virus transmission from humans to swine is far more frequent than swine-to-human zoonosis, and is central in seeding swine globally with new viral diversity. The scale of global human-to-swine transmission represents the largest 'reverse zoonosis' of a pathogen documented to date. Overcoming the bias towards perceiving swine as sources of human viruses, rather than recipients, is key to understanding how the bidirectional nature of the human-animal interface produces influenza threats to both hosts.
Keywords: evolution; human–animal interface; influenza A virus; pandemic; swine.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Scholtissek C. Pigs as the “mixing vessel” for the creation of new pandemic influenza A viruses. Med Princip Pr. 1990;2:65–71.
-
- Kida H, et al. Potential for transmission of avian influenza viruses to pigs. J Gen Virol. 1994;75:2183–2188. - PubMed
-
- Ma W, et al. The role of swine in the generation of novel influenza viruses. Zoo Pub Heal. 2009;56:326–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

