Escherichia coli antitoxin MazE as transcription factor: insights into MazE-DNA binding
- PMID: 25564525
- PMCID: PMC4333400
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku1352
Escherichia coli antitoxin MazE as transcription factor: insights into MazE-DNA binding
Abstract
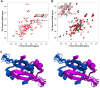
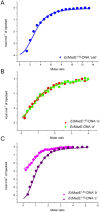
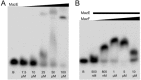
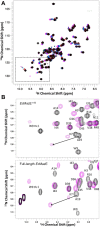
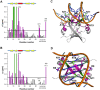
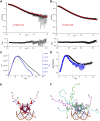
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules are pairs of genes essential for bacterial regulation upon environmental stresses. The mazEF module encodes the MazF toxin and its cognate MazE antitoxin. The highly dynamic MazE possesses an N-terminal DNA binding domain through which it can negatively regulate its own promoter. Despite being one of the first TA systems studied, transcriptional regulation of Escherichia coli mazEF remains poorly understood. This paper presents the solution structure of C-terminal truncated E. coli MazE and a MazE-DNA model with a DNA palindrome sequence ∼ 10 bp upstream of the mazEF promoter. The work has led to a transcription regulator-DNA model, which has remained elusive thus far in the E. coli toxin-antitoxin family. Multiple complementary techniques including NMR, SAXS and ITC show that the long intrinsically disordered C-termini in MazE, required for MazF neutralization, does not affect the interactions between the antitoxin and its operator. Rather, the MazE C-terminus plays an important role in the MazF binding, which was found to increase the MazE affinity for the palindromic single site operator.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
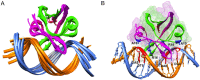

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the interactions within the mazEF addiction module of Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 22;278(34):32300-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304767200. Epub 2003 Jun 16. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12810711
-
Molecular Basis of Operator Recognition by the DNA-Binding Domain of Escherichia coli HigA Antitoxin.Biochemistry. 2025 Aug 5;64(15):3190-3202. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5c00041. Epub 2025 Jul 22. Biochemistry. 2025. PMID: 40693672
-
mazEF: a chromosomal toxin-antitoxin module that triggers programmed cell death in bacteria.J Cell Sci. 2005 Oct 1;118(Pt 19):4327-32. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02619. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16179604
-
Autoregulation of bacterial gene expression: lessons from the MazEF toxin-antitoxin system.Curr Genet. 2019 Feb;65(1):133-138. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0879-8. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30132188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mazEF-mediated programmed cell death in bacteria: "what is this?".Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015 Feb;41(1):89-100. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2013.804030. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 23799870 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and mutational analysis of MazE6-operator DNA complex provide insights into autoregulation of toxin-antitoxin systems.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 15;5(1):963. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03933-5. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36109664 Free PMC article.
-
State-of-the-art in engineering small molecule biosensors and their applications in metabolic engineering.SLAS Technol. 2024 Apr;29(2):100113. doi: 10.1016/j.slast.2023.10.005. Epub 2023 Oct 31. SLAS Technol. 2024. PMID: 37918525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification, characterization and classification of prokaryotic nucleoid-associated proteins.Mol Microbiol. 2025 Mar;123(3):206-217. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15298. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Mol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39039769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxins targeting transfer RNAs: Translation inhibition by bacterial toxin-antitoxin systems.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019 Jan;10(1):e1506. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1506. Epub 2018 Sep 16. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019. PMID: 30296016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Antisense RNA Fine-Tunes Gene Expression of the Type II MazEF Toxin-Antitoxin System.mBio. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):e0344321. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03443-21. Epub 2022 Jan 11. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35012340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bravo A., de Torrontegui G., Díaz R. Identification of components of a new stability system of plasmid R1, ParD, that is close to the origin of replication of this plasmid. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1987;210:101–110. - PubMed
-
- Gerdes K., Wagner E.G.H. RNA antitoxins. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007;10:117–124. - PubMed
-
- Buts L., Lah J., Dao-Thi M., Wyns L., Loris R. Toxin-antitoxin modules as bacterial metabolic stress managers. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005;30:672–679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

