Recognition of duplex RNA by the deaminase domain of the RNA editing enzyme ADAR2
- PMID: 25564529
- PMCID: PMC4333395
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku1345
Recognition of duplex RNA by the deaminase domain of the RNA editing enzyme ADAR2
Abstract
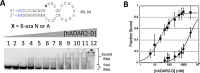
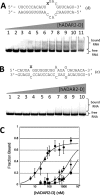
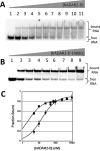
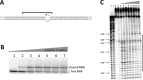
Adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs) hydrolytically deaminate adenosines (A) in a wide variety of duplex RNAs and misregulation of editing is correlated with human disease. However, our understanding of reaction selectivity is limited. ADARs are modular enzymes with multiple double-stranded RNA binding domains (dsRBDs) and a catalytic domain. While dsRBD binding is understood, little is known about ADAR catalytic domain/RNA interactions. Here we use a recently discovered RNA substrate that is rapidly deaminated by the isolated human ADAR2 deaminase domain (hADAR2-D) to probe these interactions. We introduced the nucleoside analog 8-azanebularine (8-azaN) into this RNA (and derived constructs) to mechanistically trap the protein-RNA complex without catalytic turnover for EMSA and ribonuclease footprinting analyses. EMSA showed that hADAR2-D requires duplex RNA and is sensitive to 2'-deoxy substitution at nucleotides opposite the editing site, the local sequence and 8-azaN nucleotide positioning on the duplex. Ribonuclease V1 footprinting shows that hADAR2-D protects ∼ 23 nt on the edited strand around the editing site in an asymmetric fashion (∼ 18 nt on the 5' side and ∼ 5 nt on the 3' side). These studies provide a deeper understanding of the ADAR catalytic domain-RNA interaction and new tools for biophysical analysis of ADAR-RNA complexes.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Double-stranded RNA adenosine deaminases ADAR1 and ADAR2 have overlapping specificities.Biochemistry. 2000 Oct 24;39(42):12875-84. doi: 10.1021/bi001383g. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 11041852
-
Asymmetric dimerization of adenosine deaminase acting on RNA facilitates substrate recognition.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Aug 20;48(14):7958-7972. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa532. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32597966 Free PMC article.
-
RNA sequences that direct selective ADAR editing from a SELEX library bearing 8-azanebularine.Bioorg Med Chem. 2024 Apr 15;104:117700. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.117700. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Bioorg Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38583236 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the Biological Role of Mammalian ADARs; the RNA Editing Proteins.Biomolecules. 2015 Sep 30;5(4):2338-62. doi: 10.3390/biom5042338. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 26437436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How do ADARs bind RNA? New protein-RNA structures illuminate substrate recognition by the RNA editing ADARs.Bioessays. 2017 Apr;39(4):10.1002/bies.201600187. doi: 10.1002/bies.201600187. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Bioessays. 2017. PMID: 28217931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Engineered Programmable Systems for ADAR-Mediated RNA Editing.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Mar 6;19:1065-1072. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.12.042. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32044725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of native-like crosslinked duplex RNA and study of its properties.Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 Apr 1;25(7):2191-2199. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.02.034. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28268052 Free PMC article.
-
TRIBE: Hijacking an RNA-Editing Enzyme to Identify Cell-Specific Targets of RNA-Binding Proteins.Cell. 2016 Apr 21;165(3):742-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.007. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27040499 Free PMC article.
-
A-to-I RNA editing by ADAR and its therapeutic applications: From viral infections to cancer immunotherapy.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Sep 17:e1817. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1817. Online ahead of print. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 37718249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) RNA editome by death associated protein 3 (DAP3) promotes cancer progression.Sci Adv. 2020 Jun 17;6(25):eaba5136. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba5136. eCollection 2020 Jun. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32596459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burns C.M., Chu H., Rueter S.M., Hutchinson L.K., Canton H., Sanders-Bush E., Emeson R.B. Regulation of serotonin-2C receptor G-protein coupling by RNA editing. Nature. 1997;387:303–308. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi M., Single F.N., Kohler M., Sommer B., Sprengel R., Seeburg P.H. RNA editing of AMPA receptor subunit GluR-B: a base-paired intron-exon structure determines position and efficiency. Cell. 1993;75:1361–1370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

