Genetic dissection of pheromone processing reveals main olfactory system-mediated social behaviors in mice
- PMID: 25564662
- PMCID: PMC4311817
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1416723112
Genetic dissection of pheromone processing reveals main olfactory system-mediated social behaviors in mice
Abstract
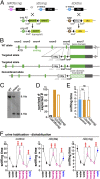
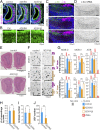
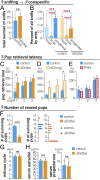
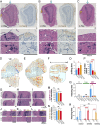
Most mammals have two major olfactory subsystems: the main olfactory system (MOS) and vomeronasal system (VNS). It is now widely accepted that the range of pheromones that control social behaviors are processed by both the VNS and the MOS. However, the functional contributions of each subsystem in social behavior remain unclear. To genetically dissociate the MOS and VNS functions, we established two conditional knockout mouse lines that led to either loss-of-function in the entire MOS or in the dorsal MOS. Mice with whole-MOS loss-of-function displayed severe defects in active sniffing and poor survival through the neonatal period. In contrast, when loss-of-function was confined to the dorsal MOB, sniffing behavior, pheromone recognition, and VNS activity were maintained. However, defects in a wide spectrum of social behaviors were observed: attraction to female urine and the accompanying ultrasonic vocalizations, chemoinvestigatory preference, aggression, maternal behaviors, and risk-assessment behaviors in response to an alarm pheromone. Functional dissociation of pheromone detection and pheromonal induction of behaviors showed the anterior olfactory nucleus (AON)-regulated social behaviors downstream from the MOS. Lesion analysis and neural activation mapping showed pheromonal activation in multiple amygdaloid and hypothalamic nuclei, important regions for the expression of social behavior, was dependent on MOS and AON functions. Identification of the MOS-AON-mediated pheromone pathway may provide insights into pheromone signaling in animals that do not possess a functional VNS, including humans.
Keywords: main olfactory system; pheromone processing; social behavior; vomeronasal system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Boehm U, Zou Z, Buck LB. Feedback loops link odor and pheromone signaling with reproduction. Cell. 2005;123(4):683–695. - PubMed
-
- Lin DY, Zhang SZ, Block E, Katz LC. Encoding social signals in the mouse main olfactory bulb. Nature. 2005;434(7032):470–477. - PubMed
-
- Yoon H, Enquist LW, Dulac C. Olfactory inputs to hypothalamic neurons controlling reproduction and fertility. Cell. 2005;123(4):669–682. - PubMed
-
- Yoshikawa K, Nakagawa H, Mori N, Watanabe H, Touhara K. An unsaturated aliphatic alcohol as a natural ligand for a mouse odorant receptor. Nat Chem Biol. 2013;9(3):160–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

