Potassium dependent rescue of a myopathy with core-like structures in mouse
- PMID: 25564733
- PMCID: PMC4309926
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.02923
Potassium dependent rescue of a myopathy with core-like structures in mouse
Abstract
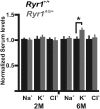
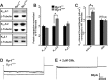
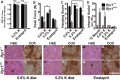
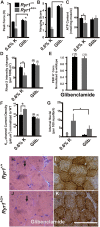
Myopathies decrease muscle functionality. Mutations in ryanodine receptor 1 (RyR1) are often associated with myopathies with microscopic core-like structures in the muscle fiber. In this study, we identify a mouse RyR1 model in which heterozygous animals display clinical and pathological hallmarks of myopathy with core-like structures. The RyR1 mutation decreases sensitivity to activated calcium release and myoplasmic calcium levels, subsequently affecting mitochondrial calcium and ATP production. Mutant muscle shows a persistent potassium leak and disrupted expression of regulators of potassium homeostasis. Inhibition of KATP channels or increasing interstitial potassium by diet or FDA-approved drugs can reverse the muscle weakness, fatigue-like physiology and pathology. We identify regulators of potassium homeostasis as biomarkers of disease that may reveal therapeutic targets in human patients with myopathy of central core disease (CCD). Altogether, our results suggest that amelioration of potassium leaks through potassium homeostasis mechanisms may minimize muscle damage of myopathies due to certain RyR1 mutations.
Keywords: KATP channel; cell biology; congenital myopathy; human; mouse; potassium homeostasis; ryanodine receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Andrade F, Trujillo X, Sánchez-Pastor E, Montoya-Pérez R, Saavedra-Molina A, Ortiz-Mesina M, Huerta M. Glibenclamide increases post-fatigue tension in slow skeletal muscle fibers of the chicken. Journal of Comparative Physiology B, Biochemical, Systemic, and Environmental Physiology. 2011;181:403–412. doi: 10.1007/s00360-010-0527-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baczkó I, Jones L, McGuigan CF, Manning Fox JE, Gandhi M, Giles WR, Clanachan AS, Light PE. Plasma membrane KATP channel-mediated cardioprotection involves posthypoxic reductions in calcium overload and contractile dysfunction: mechanistic insights into cardioplegia. FASEB Journal. 2005;19:980–982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

