Crystallographic and spectroscopic snapshots reveal a dehydrogenase in action
- PMID: 25565451
- PMCID: PMC4286809
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6935
Crystallographic and spectroscopic snapshots reveal a dehydrogenase in action
Abstract
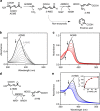
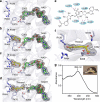
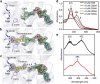
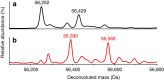
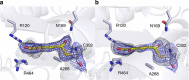
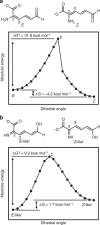
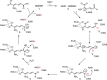
Aldehydes are ubiquitous intermediates in metabolic pathways and their innate reactivity can often make them quite unstable. There are several aldehydic intermediates in the metabolic pathway for tryptophan degradation that can decay into neuroactive compounds that have been associated with numerous neurological diseases. An enzyme of this pathway, 2-aminomuconate-6-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, is responsible for 'disarming' the final aldehydic intermediate. Here we show the crystal structures of a bacterial analogue enzyme in five catalytically relevant forms: resting state, one binary and two ternary complexes, and a covalent, thioacyl intermediate. We also report the crystal structures of a tetrahedral, thiohemiacetal intermediate, a thioacyl intermediate and an NAD(+)-bound complex from an active site mutant. These covalent intermediates are characterized by single-crystal and solution-state electronic absorption spectroscopy. The crystal structures reveal that the substrate undergoes an E/Z isomerization at the enzyme active site before an sp(3)-to-sp(2) transition during enzyme-mediated oxidation.
Figures
References
-
- Keszthelyi D., Troost F. J. & Masclee A. A. Understanding the role of tryptophan and serotonin metabolism in gastrointestinal function. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 21, 1239–1249 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Myint A. M. et al.. Kynurenine pathway in major depression: evidence of impaired neuroprotection. J. Affect. Disord. 98, 143–151 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Ogawa T. et al.. Kynurenine pathway abnormalities in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 42, 1702–1706 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Guillemin G. J. et al.. Quinolinic acid in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 527, 167–176 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Guidetti P. & Schwarcz R. 3-Hydroxykynurenine and quinolinate: pathogenic synergism in early grade Huntington’s disease? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 527, 137–145 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

