Endodontic management of maxillary first molar with seven root canals diagnosed using Cone Beam Computed Tomography scanning
- PMID: 25565745
- PMCID: PMC4213875
- DOI: 10.4103/0975-962X.140837
Endodontic management of maxillary first molar with seven root canals diagnosed using Cone Beam Computed Tomography scanning
Abstract
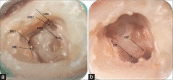
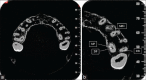
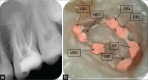
The main objective of root canal treatment is thorough cleaning and shaping of the entire pulp space and its complete filling with an inert filling material. A major cause of post-treatment disease is the inability to locate, debride or adequately fill all canals of the root canal system. The form, configuration, and number of root canals in the maxillary first molars have been discussed for more than half a century. Maxillary first molars commonly present with three roots and three canals, with a second mesiobuccal canal (MB2) also present. With the advent of improved magnification there are reports of multiple root canals in the maxillary first molars. Nonsurgical endodontic therapy of a left maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals was successfully performed under a dental operating microscope. The diagnosis of multiple root canals was confirmed with the help of Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) images.
Keywords: Aberrant canal anatomy; cone beam computed tomography; dental operating microscope; maxillary first molar.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- European Society of Endodontology. Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: Consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology. Int Endod J. 2002;39:921–30. - PubMed
-
- Vertucci FJ. Root canal morphology and its relationship to endodontic procedures. Endod Topics. 2005;10:3–29.
-
- Friedman S. Prognosis of initial endodontic therapy. Endod Topics. 2002;2:59–88.
-
- Seidberg BH, Altman M, Guttuso J, Susan M. Frequency of two mesiobuccal root canals in maxillary permanent first molars. J Am Dent Assoc. 1973;87:852–6. - PubMed
-
- Alavi AM, Opasanon A, Ng YL, Gulabivala K. Root and canal morphology of Thai maxillary molars. Int Endod J. 2002;35:478–85. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources