Role of NG2 expressing cells in addiction: a new approach for an old problem
- PMID: 25566075
- PMCID: PMC4271769
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00279
Role of NG2 expressing cells in addiction: a new approach for an old problem
Abstract
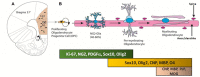
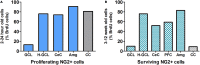
Neuron-glial antigen 2 (NG2) is a proteoglycan expressed predominantly in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs). NG2-expressing OPCs (NG2-OPCs) are self-renewing cells that are widely distributed in the gray and white matter areas of the central nervous system. NG2-OPCs can mature into premyelinating oligodendrocytes and myelinating oligodendroglia which serve as the primary source of myelin in the brain. This review characterizes NG2-OPCs in brain structure and function, conceptualizes the role of NG2-OPCs in brain regions associated with negative reinforcement and relapse to drug seeking and discusses how NG2-OPCs are regulated by neuromodulators linked to motivational withdrawal. We hope to provide the readers with an overview of the role of NG2-OPCs in brain structure and function in the context of negative affect state in substance abuse disorders and to integrate our current understanding of the physiological significance of the NG2-OPCs in the adult brain.
Keywords: BrdU; NG2; amygdala; hippocampus; prefrontal cortex; progenitors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NG2-expressing glial progenitor cells: an abundant and widespread population of cycling cells in the adult rat CNS.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003 Oct;24(2):476-88. doi: 10.1016/s1044-7431(03)00210-0. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14572468
-
The response of NG2-expressing oligodendrocyte progenitors to demyelination in MOG-EAE and MS.J Neurocytol. 2002 Jul-Aug;31(6-7):523-36. doi: 10.1023/a:1025747832215. J Neurocytol. 2002. PMID: 14501221
-
Evidence that perinatal and adult NG2-glia are not conventional oligodendrocyte progenitors and do not depend on axons for their survival.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003 Aug;23(4):544-58. doi: 10.1016/s1044-7431(03)00176-3. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12932436
-
NG2-expressing cells as oligodendrocyte progenitors in the normal and demyelinated adult central nervous system.J Anat. 2005 Dec;207(6):707-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00454.x. J Anat. 2005. PMID: 16367798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiology of Oligodendroglia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1175:117-128. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-9913-8_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31583586 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Glial Cells in Neuronal Function, Mood Disorders, and Drug Addiction.Brain Sci. 2024 May 30;14(6):558. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14060558. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyper-oligodendrogenesis at the vascular niche and reduced blood-brain barrier integrity in the prefrontal cortex during protracted abstinence.Neuroscience. 2017 Oct 24;362:265-271. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.08.048. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 28870701 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Exercise as a Therapeutic Intervention for Methamphetamine Addiction-Like Behavior.Brain Plast. 2015 Oct 9;1(1):63-81. doi: 10.3233/BPL-150007. Brain Plast. 2015. PMID: 29765835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function and Mechanism of Myelin Regulation in Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.Bioessays. 2019 Jul;41(7):e1800255. doi: 10.1002/bies.201800255. Epub 2019 May 16. Bioessays. 2019. PMID: 31094014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult oligodendrocyte progenitor cells - Multifaceted regulators of the CNS in health and disease.Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Oct;57:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.01.005. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Brain Behav Immun. 2016. PMID: 26796621 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

