β3-adrenoceptors inhibit stimulated norepinephrine release in spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 25566095
- PMCID: PMC4271585
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00499
β3-adrenoceptors inhibit stimulated norepinephrine release in spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
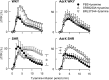
Here, the influence of β3-adrenoceptors on catecholamine release in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats was analyzed. Blood pressure was recorded through a femoral artery catheter, and cardiac output by ascending aorta flow. Time from onset of flow to maximum rise in flow indicated inotropy. Total peripheral vascular resistance (TPR) was calculated. Norepinephrine release was stimulated with tyramine, which allowed presynaptic release-control to be reflected as changes in the plasma norepinephrine concentration. β3-adrenoceptor agonist (BRL37344) reduced baseline vascular resistance, the tyramine-stimulated norepinephrine overflow and the positive inotropic response to tyramine in hypertensive but not normotensive rats. β3-adrenoceptor antagonist (SR59230A) reduced tyramine-stimulated norepinephrine release in both strains and the secretion of epinephrine in hypertensive rats. SR59230A reduced tyramine-induced tachycardia in normotensive rats, and prevented down-regulation of the tyramine-induced rise in resistance in hypertensive rats. It was concluded that the contradicting results obtained by agonist vs. antagonist, could be explained by their interaction with two different β-adrenoceptors: The BRL37344-dependent inhibition of stimulated norepinephrine release and positive inotropic response to tyramine was compatible with stimulation of β3-adrenoceptor coupling to inhibitory G-protein. This was observed only in hypertensive rats during stimulated, high levels of circulating catecholamines. The effect of BRL37344 on baseline vascular resistance was compatible with activation of β3-adrenoceptor coupling to endothelial nitric oxide synthase. The inhibitory effect of SR59230A on tyramine-stimulated norepinephrine release in both strains, the increased TPR-response to tyramine in hypertensive rats and tachycardia in normotensive rats may result from inhibition of the low-affinity-state β1-adrenoceptor, also known as the putative β4-adrenoceptor.
Keywords: epinephrine secretion; hypertension; norepinephrine release; putative β4-adrenoceptors; β3-adrenoceptors.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

