A hand hygiene intervention to reduce infections in child daycare: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 25566827
- PMCID: PMC4531476
- DOI: 10.1017/S095026881400329X
A hand hygiene intervention to reduce infections in child daycare: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
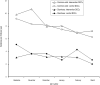
Infections are common in children attending daycare centres (DCCs). We evaluated the effect of a hand hygiene (HH) intervention for caregivers on the incidence of gastrointestinal and respiratory infections in children. The intervention was evaluated in a two-arm cluster randomized controlled trial. Thirty-six DCCs received the intervention including HH products, training sessions, and posters/stickers. Thirty-five control DCCs continued usual practice. Incidence of episodes of diarrhoea and the common cold in children was monitored by parents during 6 months. Using multilevel Poisson regression, incidence rate ratios (IRRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were obtained. Diarrhoeal incidence was monitored in 545 children for 91 937 days. During follow-up, the incidence was 3·0 episodes per child-year in intervention DCCs vs. 3·4 in control DCCs (IRR 0·90, 95% CI 0·73-1·11). Incidence of the common cold was monitored in 541 children for 91 373 days. During follow-up, the incidence was 8·2 episodes per child-year in intervention DCCs vs. 7·4 in control DCCs (IRR 1·07, 95% CI 0·97-1·19). In this study, no evidence for an effect of the intervention was demonstrated on the incidence of episodes of diarrhoea and the common cold.
Keywords: Cold (common); gastroenteritis; hand hygiene; hygiene – professional; infectious disease control.
Figures
References
-
- Zutavern A, et al. Day care in relation to respiratory-tract and gastrointestinal infections in a German birth cohort study. Acta Paediatrica 2007; 96: 1494–1499. - PubMed
-
- Barros AJ. Child-care attendance and common morbidity: evidence of association in the literature and questions of design. Revista de Saude Publica 1999; 33: 98–106. - PubMed
-
- Ejemot RI, et al. Hand washing for preventing diarrhoea. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008. Art. no. CD004265. Issue no. 1. - PubMed
-
- Zomer TP, et al. Hand hygiene compliance and environmental determinants in child day care centers: an observational study. American Journal of Infection Control 2013; 41: 497–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical