Effect of a moderate fat diet with and without avocados on lipoprotein particle number, size and subclasses in overweight and obese adults: a randomized, controlled trial
- PMID: 25567051
- PMCID: PMC4330060
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001355
Effect of a moderate fat diet with and without avocados on lipoprotein particle number, size and subclasses in overweight and obese adults: a randomized, controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Avocados are a nutrient-dense source of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) that can be used to replace saturated fatty acids (SFA) in a diet to lower low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Well-controlled studies are lacking on the effect of avocado consumption on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors.
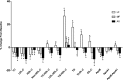
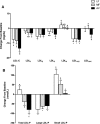
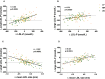
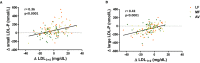
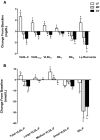
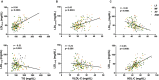
Methods and results: A randomized, crossover, controlled feeding trial was conducted with 45 overweight or obese participants with baseline LDL-C in the 25th to 90th percentile. Three cholesterol-lowering diets (6% to 7% SFA) were fed (5 weeks each): a lower-fat diet (LF: 24% fat); 2 moderate-fat diets (34% fat) provided similar foods and were matched for macronutrients and fatty acids: the avocado diet (AV) included one fresh Hass avocado (136 g) per day, and the moderate-fat diet (MF) mainly used high oleic acid oils to match the fatty acid content of one avocado. Compared with baseline, the reduction in LDL-C and non-high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol on the AV diet (-13.5 mg/dL, -14.6 mg/dL) was greater (P<0.05) than the MF (-8.3 mg/dL, -8.7 mg/dL) and LF (-7.4 mg/dL, -4.8 mg/dL) diets. Furthermore, only the AV diet significantly decreased LDL particle number (LDL-P, -80.1 nmol/L, P=0.0001), small dense LDL cholesterol (LDL(3+4), -4.1 mg/dL, P=0.04), and the ratio of LDL/HDL (-6.6%, P<0.0001) from baseline.
Conclusions: Inclusion of one avocado per day as part of a moderate-fat, cholesterol-lowering diet has additional LDL-C, LDL-P, and non-HDL-C lowering effects, especially for small, dense LDL. Our results demonstrate that avocados have beneficial effects on cardio-metabolic risk factors that extend beyond their heart-healthy fatty acid profile.
Clinical trial registration url: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT01235832.
Keywords: MUFA; avocados; cardiovascular disease; diet; fatty acids; lipids; lipoproteins.
© 2015 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Moderate-Fat Diet with One Avocado per Day Increases Plasma Antioxidants and Decreases the Oxidation of Small, Dense LDL in Adults with Overweight and Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Nutr. 2020 Feb 1;150(2):276-284. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz231. J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31616932 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exercise attenuates the increase in plasma monounsaturated fatty acids and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol but not high-density lipoprotein 2b cholesterol caused by high-oleic ground beef in women.Nutr Res. 2013 Dec;33(12):1003-11. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Nutr Res. 2013. PMID: 24267039 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of high-fat and low-fat diets rich in monounsaturated fatty acids on serum lipids, LDL size and indices of lipid peroxidation in healthy non-obese men and women when consumed under controlled conditions.Eur J Nutr. 2011 Feb;50(1):71-9. doi: 10.1007/s00394-010-0116-9. Epub 2010 Jun 3. Eur J Nutr. 2011. PMID: 20521076 Clinical Trial.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Hass Avocado Clinical Trials, Observational Studies, and Biological Mechanisms.Nutrients. 2021 Dec 7;13(12):4376. doi: 10.3390/nu13124376. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34959933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Avocado Consumption and Cardiometabolic Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2024 Feb;124(2):233-248.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2022.12.008. Epub 2022 Dec 21. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2024. PMID: 36565850
Cited by
-
Avocado Consumption for 12 Weeks and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and Insulin Resistance.J Nutr. 2022 Aug 9;152(8):1851-1861. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxac126. J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35700149 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Avocado Consumption Increases Macular Pigment Density in Older Adults: A Randomized, Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2017 Aug 23;9(9):919. doi: 10.3390/nu9090919. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28832514 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Pulp, Peel, Seed, and Food Products of Persea americana as Sources of Bioactive Phytochemicals with Cardioprotective Properties: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 19;25(24):13622. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413622. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-genetic influences on lipoprotein(a) concentrations.Atherosclerosis. 2022 May;349:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.04.006. Atherosclerosis. 2022. PMID: 35606076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Avocado Consumption Alters Gastrointestinal Bacteria Abundance and Microbial Metabolite Concentrations among Adults with Overweight or Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Nutr. 2021 Apr 8;151(4):753-762. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxaa219. J Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32805028 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Eckel RH, Jakicic JM, Ard JD, Miller NH, Hubbard VS, Nonas CA, de Jesus JM, Sacks FM, Lee I‐M, Lichtenstein AH, Loria CM, Millen BE, Miller NH, Nonas CA, Sacks FM, Smith SC, Jr, Svetkey LP, Wadden TW, Yanovski SZ. AHA/ACC guideline on lifestyle management to reduce cardiovascular risk: a report of the ACC/AHA task force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013; 2013:1524-4539. - PubMed
-
- Moreno JJ, Mitjavila MT. The degree of unsaturation of dietary fatty acids and the development of atherosclerosis (review). J Nutr Biochem. 2003; 14:182-195. - PubMed
-
- Estruch R, Ros E, Salas‐Salvadó J, Covas M‐I, Corella D, Arós F, Gómez‐Gracia E, Ruiz‐Gutiérrez V, Fiol M, Lapetra J. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean diet. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:1279-1290. - PubMed
-
- Carranza‐Madrigal J, Herrera‐Abarca JE, Alvizouri‐Muoz M, Alvarado‐Jimenez MR, Chavez‐Carbajal F. Effects of a vegetarian diet vs. A vegetarian diet enriched with avocado in hypercholesterolemic patients. Arch Med Res. 1997; 28:537-542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

