Early-life physical activity reverses metabolic and Foxo1 epigenetic misregulation induced by gestational sleep disturbance
- PMID: 25568076
- PMCID: PMC4346758
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00426.2014
Early-life physical activity reverses metabolic and Foxo1 epigenetic misregulation induced by gestational sleep disturbance
Abstract
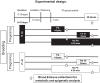
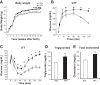
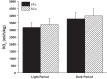
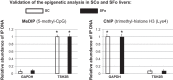
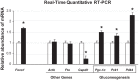
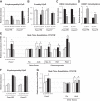
Sleep disorders are highly prevalent during late pregnancy and can impose adverse effects, such as preeclampsia and diabetes. However, the consequences of sleep fragmentation (SF) on offspring metabolism and epigenomic signatures are unclear. We report that physical activity during early life, but not later, reversed the increased body weight, altered glucose and lipid homeostasis, and increased visceral adipose tissue in offspring of mice subjected to gestational SF (SFo). The reversibility of this phenotype may reflect epigenetic mechanisms induced by SF during gestation. Accordingly, we found that the metabolic master switch Foxo1 was epigenetically misregulated in SFo livers in a temporally regulated fashion. Temporal Foxo1 analysis and its gluconeogenetic targets revealed that the epigenetic abnormalities of Foxo1 precede the metabolic syndrome phenotype. Importantly, regular physical activity early, but not later in life, reversed Foxo1 epigenetic misregulation and altered the metabolic phenotype in gestationally SF-exposed offspring. Thus, we have identified a restricted postnatal period during which lifestyle interventions may reverse the Foxo1 epigenetically mediated risk for metabolic dysfunction later in the life, as induced by gestational sleep disorders.
Keywords: Foxo1 gene; epigenetics; offspring metabolism effect; physical activity; pregnancy sleep disruption; reverse epigenetic effects.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures






References
-
- Barres R, Yan J, Egan B, Treebak JT, Rasmussen M, Fritz T, Caidahl K, Krook A, O'Gorman DJ, Zierath JR. Acute exercise remodels promoter methylation in human skeletal muscle. Cell Metab 15: 405–411, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Bateson P, Barker D, Clutton-Brock T, Deb D, D'Udine B, Foley RA, Gluckman P, Godfrey K, Kirkwood T, Lahr MM, McNamara J, Metcalfe NB, Monaghan P, Spencer HG, Sultan SE. Developmental plasticity and human health. Nature 430: 419–421, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

