Pathogenesis and treatment of falls in elderly
- PMID: 25568657
- PMCID: PMC4269147
Pathogenesis and treatment of falls in elderly
Abstract
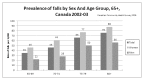
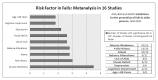
Falls in the elderly are a public health problem. Consequences of falls are increased risk of hospitalization, which results in an increase in health care costs. It is estimated that 33% of individuals older than 65 years undergoes falls. Causes of falls can be distinguished in intrinsic and extrinsic predisposing conditions. The intrinsic causes can be divided into age-related physiological changes and pathological predisposing conditions. The age-related physiological changes are sight disorders, hearing disorders, alterations in the Central Nervous System, balance deficits, musculoskeletal alterations. The pathological conditions can be Neurological, Cardiovascular, Endocrine, Psychiatric, Iatrogenic. Extrinsic causes of falling are environmental factors such as obstacles, inadequate footwear. The treatment of falls must be multidimensional and multidisciplinary. The best instrument in evaluating elderly at risk is Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA). CGA allows better management resulting in reduced costs. The treatment should be primarily preventive acting on extrinsic causes; then treatment of chronic and acute diseases. Rehabilitation is fundamental, in order to improve residual capacity, motor skills, postural control, recovery of strength. There are two main types of exercises: aerobic and muscular strength training. Education of patient is a key-point, in particular through the Back School. In conclusion falls in the elderly are presented as a "geriatric syndrome"; through a multidimensional assessment, an integrated treatment and a rehabilitation program is possible to improve quality of life in elderly.
Keywords: comprehensive geriatric assessment; elderly; falls; multidimensional assessment.
Figures
References
-
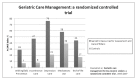
- Rubenstein LZ, Robbins AS, Josephson KR, et al. The value of assessing falls in an elderly population. A randomized clinical trial. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1990;113:308–16. - PubMed
-
- Gill TM, Allore HG, Holford TR, Guo Z. Hospitalization, restricted activity, and the development of disability among older persons. The Journal of American Medical Association. 2004;292(17):2115–2124. - PubMed
-
- Tinetti ME. Preventing falls in elderly persons. New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;348:42–49. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
