Cerebral near infrared spectroscopy oximetry in extremely preterm infants: phase II randomised clinical trial
- PMID: 25569128
- PMCID: PMC4283997
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.g7635
Cerebral near infrared spectroscopy oximetry in extremely preterm infants: phase II randomised clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: To determine if it is possible to stabilise the cerebral oxygenation of extremely preterm infants monitored by cerebral near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) oximetry.
Design: Phase II randomised, single blinded, parallel clinical trial.
Setting: Eight tertiary neonatal intensive care units in eight European countries.
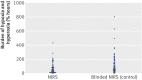
Participants: 166 extremely preterm infants born before 28 weeks of gestation: 86 were randomised to cerebral NIRS monitoring and 80 to blinded NIRS monitoring. The only exclusion criterion was a decision not to provide life support.
Interventions: Monitoring of cerebral oxygenation using NIRS in combination with a dedicated treatment guideline during the first 72 hours of life (experimental) compared with blinded NIRS oxygenation monitoring with standard care (control).
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome measure was the time spent outside the target range of 55-85% for cerebral oxygenation multiplied by the mean absolute deviation, expressed in %hours (burden of hypoxia and hyperoxia). One hour with an oxygenation of 50% gives 5%hours of hypoxia. Secondary outcomes were all cause mortality at term equivalent age and a brain injury score assessed by cerebral ultrasonography.
Randomisation: Allocation sequence 1:1 with block sizes 4 and 6 in random order concealed for the investigators. The allocation was stratified for gestational age (<26 weeks or ≥ 26 weeks).
Blinding: Cerebral oxygenation measurements were blinded in the control group. All outcome assessors were blinded to group allocation.
Results: The 86 infants randomised to the NIRS group had a median burden of hypoxia and hyperoxia of 36.1%hours (interquartile range 9.2-79.5%hours) compared with 81.3 (38.5-181.3) %hours in the control group, a reduction of 58% (95% confidence interval 35% to 73%, P<0.001). In the experimental group the median burden of hypoxia was 16.6 (interquartile range 5.4-68.1) %hours, compared with 53.6 (17.4-171.3) %hours in the control group (P=0.0012). The median burden of hyperoxia was similar between the groups: 1.2 (interquartile range 0.3-9.6) %hours in the experimental group compared with 1.1 (0.1-23.4) %hours in the control group (P=0.98). We found no statistically significant differences between the two groups at term corrected age. No severe adverse reactions were associated with the device.
Conclusions: Cerebral oxygenation was stabilised in extremely preterm infants using a dedicated treatment guideline in combination with cerebral NIRS monitoring.Trial registration ClinicalTrial.gov NCT01590316.
© Hyttel-Sorensen et al 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures


References
-
- Hansen B, Hoff B, Greisen G, Mortensen EL for the Danish ETFOL study group. Early nasal continuous positive airway pressure in a cohort of the smallest infants in Denmark: neurodevelopmental outcome at five years of age. Acta Paediatrica 2004;93:190-5. - PubMed
-
- Noori S, Stavroudis TA, Seri I. Systemic and cerebral hemodynamics during the transitional period after premature birth. Clin Perinatol 2009;36:723-36-v. - PubMed
-
- Hunt RW, Evans N, Rieger I, Kluckow M. Low superior vena cava flow and neurodevelopment at 3 years in very preterm infants. J Pediatr 2004;145:588-92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
