The global regulatory architecture of transcription during the Caulobacter cell cycle
- PMID: 25569173
- PMCID: PMC4287350
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004831
The global regulatory architecture of transcription during the Caulobacter cell cycle
Abstract
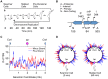
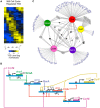
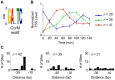
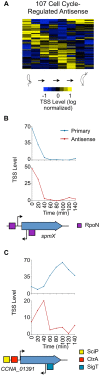
Each Caulobacter cell cycle involves differentiation and an asymmetric cell division driven by a cyclical regulatory circuit comprised of four transcription factors (TFs) and a DNA methyltransferase. Using a modified global 5' RACE protocol, we globally mapped transcription start sites (TSSs) at base-pair resolution, measured their transcription levels at multiple times in the cell cycle, and identified their transcription factor binding sites. Out of 2726 TSSs, 586 were shown to be cell cycle-regulated and we identified 529 binding sites for the cell cycle master regulators. Twenty-three percent of the cell cycle-regulated promoters were found to be under the combinatorial control of two or more of the global regulators. Previously unknown features of the core cell cycle circuit were identified, including 107 antisense TSSs which exhibit cell cycle-control, and 241 genes with multiple TSSs whose transcription levels often exhibited different cell cycle timing. Cumulatively, this study uncovered novel new layers of transcriptional regulation mediating the bacterial cell cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Collier J (2012) Regulation of chromosomal replication in Caulobacter crescentus . Plasmid 67: 76–87. - PubMed
-
- McAdams HH, Shapiro L (2003) A bacterial cell-cycle regulatory network operating in time and space. Science 301: 1874–1877. - PubMed
-
- Kirkpatrick CL, Viollier PH (2012) Decoding Caulobacter development . FEMS Microbiol Rev 36: 193–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

