Nortriptyline for neuropathic pain in adults
- PMID: 25569864
- PMCID: PMC6485407
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011209.pub2
Nortriptyline for neuropathic pain in adults
Abstract
Background: Antidepressants are widely used to treat chronic neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage), usually in doses below those at which they exert antidepressant effects. An earlier review that included all antidepressants for neuropathic pain is being replaced by new reviews of individual drugs examining individual neuropathic pain conditions.Nortriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant that is occasionally used for treating neuropathic pain, and is recommended in European, UK, and USA guidelines.
Objectives: To assess the analgesic efficacy and associated adverse events of nortriptyline for chronic neuropathic pain in adults.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, and EMBASE from inception to 7 January 2015, and the reference lists of retrieved papers and other reviews. We also searched two clinical trials databases for ongoing or unpublished studies.
Selection criteria: We included randomised, double-blind studies of at least two weeks' duration comparing nortriptyline with placebo or another active treatment in chronic neuropathic pain. Participants were adults aged 18 years and over. We included only full journal publication articles and clinical trial summaries.
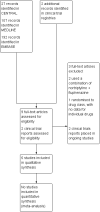
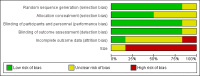
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted efficacy and adverse event data, and examined issues of study quality. We considered the evidence using three tiers. First tier evidence derived from data meeting current best standards and subject to minimal risk of bias (outcome equivalent to substantial pain intensity reduction, intention-to-treat analysis without imputation for dropouts; at least 200 participants in the comparison, 8 to 12 weeks' duration, parallel design); second tier evidence from data that failed to meet one or more of these criteria and were considered at some risk of bias but with adequate numbers in the comparison; and third tier evidence from data involving small numbers of participants that was considered very likely to be biased or used outcomes of limited clinical utility, or both.We planned to calculate risk ratio (RR) and numbers needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNT) and harmful outcome (NNH) using standard methods expected by The Cochrane Collaboration.
Main results: We included six studies treating 310 participants (mean or median age 49 to 64 years) with various neuropathic pain conditions. Five studies used a cross-over design, and one used a parallel-group design; 272 participants were randomised to treatment with nortriptyline, 145 to placebo, 94 to gabapentin, 56 to gabapentin plus nortriptyline, 55 to morphine, 55 to morphine plus nortriptyline, 39 to chlorimipramine, and 33 to amitriptyline. Treatment periods lasted from three to eight weeks. All studies had one or more sources of potential major bias.No study provided first or second tier evidence for any outcome. Only one study reported our primary outcome of people with at least 50% reduction in pain. There was no indication that either nortriptyline or gabapentin was more effective in postherpetic neuralgia (very low quality evidence). Two studies reported the number of people with at least moderate pain relief, and one reported the number who were satisfied with their pain relief and had tolerable adverse effects. We considered these outcomes to be equivalent to our other primary outcome of Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) much or very much improved.We could not pool data, but third tier evidence in individual studies indicated similar efficacy to other active interventions (gabapentin, morphine, chlorimipramine, and amitriptyline), and to placebo in the conditions studied (very low quality evidence). Adverse event reporting was inconsistent and fragmented. More participants reported adverse events with nortriptyline than with placebo, similar numbers with nortriptyline and other antidepressants (amitriptyline and chlorimipramine) and gabapentin, and slightly more with morphine (very low quality evidence). No study reported any serious adverse events or deaths.
Authors' conclusions: We found little evidence to support the use of nortriptyline to treat the neuropathic pain conditions included in this review. There were no studies in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. The studies were methodologically flawed, largely due to small size, and potentially subject to major bias. The results of this review do not support the use of nortriptyline as a first line treatment. Effective medicines with much greater supportive evidence are available, such as duloxetine and pregabalin.
Conflict of interest statement
The review authors have no known conflicts of interest.
Figures
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Chandra 2006 {published data only}
-
- Chandra K1, Shafiq N, Pandhi P, Gupta S, Malhotra S. Gabapentin versus nortriptyline in post‐herpetic neuralgia patients: a randomized, double‐blind clinical trial‐‐the GONIP Trial. International journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2006;44(8):358‐63. [PUBMED: 16961166] - PubMed
Gilron 2009 {published data only}
-
- Block JP. Combined treatment with gabapentin and nortriptyline improves pain control in peripheral neuropathy more than either agent alone. Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management 2009;16(12):544‐45.
Hammack 2002 {published data only}
Khoromi 2007 {published data only}
Panerai 1990 {published data only}
-
- Panerai AE, Monza G, Movilia P, Bianchi M, Francucci BM, Tiengo M. A randomized, within‐patient, cross‐over, placebo‐controlled trial on the efficacy and tolerability of the tricyclic antidepressants chlorimipramine and nortriptyline in central pain. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1990;82(1):34‐8. [PUBMED: 2239134] - PubMed
Watson 1998 {published data only}
-
- Watson CP, Vernich L, Chipman M, Reed K. Nortriptyline versus amitriptyline in postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized trial. Neurology 1998;51(4):1166‐71. [PUBMED: 9781549] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Gómez‐Pérez 1985 {published data only}
-
- Gómez‐Pérez FJ, Rull JA, Dies H, Rodriquez‐Rivera JG, Gonzalez‐Barranco J, Lozano‐Castañeda O. Nortriptyline and fluphenazine in the symptomatic treatment of diabetic neuropathy. A double‐blind cross‐over study. Pain 1985;23(4):395‐400. [PUBMED: 3911140] - PubMed
Gómez‐Pérez 1986 {published data only}
-
- Gómez‐Pérez FJ, Choza R, Ríos JM, Reza A, Huerta E, Aguilar CA, et al. Nortriptyline‐fluphenazine vs. carbamazepine in the symptomatic treatment of diabetic neuropathy. Archives of Medical Research 1986;27(4):525‐9. [PUBMED: 8987189] - PubMed
Raja 2002 {published data only}
-
- Phase III randomized controlled study of morphine and nortriptyline in the management of postherpetic neuralgia. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00004390?term=NCT00004390&rank=1 (accessed 10 June 2014). [NCT00004390]
References to ongoing studies
ACTRN12612001304820 {published data only}
-
- Chisholm C (Principle investigator). High versus low dose Nortriptyline for pain control and sleep in the presence of radicular back pain. www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12612001304820.aspx (accessed 1 July 2014). [ACTRN12612001304820]
ISRCTN04803491 {unpublished data only}
-
- Gilron I (Principle investigator). A double‐blind, randomised controlled trial of nortriptyline, morphine, and their combination for neuropathic pain. www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN04803491 (accessed 1 July 2014).
Additional references
Attal 2010
Baron 2010
Baron 2012
Bouhassira 2008
Chronicle 2004
Derry 2012
Derry 2013
Derry 2014
Di Franco 2010
-
- Franco M, Iannuccelli C, Atzeni F, Cazzola M, Salaffi F, Valesini G, et al. Pharmacological treatment of fibromyalgia. Clinical and experimental Rheumatology 2010;28(6 Suppl63):S110‐6. - PubMed
Dick 2007
-
- Dick IE, Brochu RM, Purohit Y, Kaczorowski GJ, Martin WJ, Priest BT. Sodium channel blockade may contribute to the analgesic efficacy of antidepressants. Journal of Pain 2007;8(4):315‐24. [10.1016/j.jpain.2006.10.001] - PubMed
Dworkin 2008
Dworkin 2010
Elbourne 2002
Gustorff 2008
Hall 2008
Hearn 2014
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17(1):1‐12. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Jensen 2011
Kalso 2013
Katusic 1991
-
- Katusic S, Williams DB, Beard CM, Bergstralh EJ, Kurland LT. Epidemiology and clinical features of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: similarities and differences, Rochester, Minnesota,1945‐1984. Neuroepidemiology 1991;10:276‐81. - PubMed
Khan 1996
-
- Khan KS, Daya S, Jadad A. The importance of quality of primary studies in producing unbiased systematic reviews. Archives of Internal Medicine 1996;156(6):661‐6. - PubMed
Koopman 2009
L'Abbé 1987
-
- L'Abbé KA, Detsky AS, O'Rourke K. Meta‐analysis in clinical research. Annals of Internal Medicine 1987;107:224‐33. - PubMed
Lunn 2014
McQuay 1998
-
- McQuay H, Moore R. An evidence‐based resource for pain relief. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998.
McQuay 2007
-
- McQuay HJ, Smith LA, Moore RA. Chronic Pain. In: Stevens A, Raftery J, Mant J, Simpson S editor(s). Health Care Needs Assessment. 3rd Edition. Oxford: Radcliffe Publishing, 2007. [ISBN: 978‐1‐84619‐063‐6]
Moisset 2007
Moore 1998
Moore 2008
-
- Moore RA, Barden J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Managing potential publication bias. In: McQuay HJ, Kalso E, Moore RA editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Pain Research: Methodology Refined. Seattle: IASP Press, 2008:15‐24. [ISBN: 978–0–931092–69–5]
Moore 2009
Moore 2010a
-
- Moore RA, Eccleston C, Derry S, Wiffen P, Bell RF, Straube S, et al. "Evidence" in chronic pain ‐ establishing best practice in the reporting of systematic reviews. Pain 2010;150(3):386‐9. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Moore 2010b
Moore 2010c
-
- Moore RA, Moore OA, Derry S, Peloso PM, Gammaitoni AR, Wang H. Responder analysis for pain relief and numbers needed to treat in a meta‐analysis of etoricoxib osteoarthritis trials: bridging a gap between clinical trials and clinical practice. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69(2):374‐9. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Moore 2010d
-
- Moore RA, Smugar SS, Wang H, Peloso PM, Gammaitoni A. Numbers‐needed‐to‐treat analyses‐‐do timing, dropouts, and outcome matter? Pooled analysis of two randomized, placebo‐controlled chronic low back pain trials. Pain 2010;151(3):592‐7. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Moore 2011a
-
- Moore RA, Straube S, Paine J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Minimum efficacy criteria for comparisons between treatments using individual patient meta‐analysis of acute pain trials: examples of etoricoxib, paracetamol, ibuprofen, and ibuprofen/paracetamol combinations after third molar extraction. Pain 2011;152(5):982‐9. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Moore 2011b
Moore 2012a
Moore 2012b
Moore 2013a
Moore 2013b
Moore 2014a
Moore 2014b
Moore 2014c
NICE 2013
-
- NICE clinical guideline 173. Neuropathic pain – pharmacological management. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG173 (accessed 24 March 2014) 2013:1‐138.
Nüesch 2010
O'Brien 2010
O'Connor 2009
Onghena 1992
-
- Onghena P, Houdenhove B. Antidepressant‐induced analgesia in chronic non‐malignant pain: a meta‐analysis of 39 placebo‐controlled studies. Pain 1992;49:205‐20. - PubMed
PaPaS 2012
-
- PaPaS author and referee guidance. http://papas.cochrane.org/papas‐documents (accessed 22 January 2013).
PCA 2014
-
- Prescribing and Primary Care team, Health and Social Care Information Centre. Prescription cost analysis, England 2013. Health and Social Care Information Centre, 2014. [ISBN: 978‐1‐78386‐089‐0]
Rappaport 1994
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Soni 2013
Straube 2008
-
- Straube S, Derry S, McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Enriched enrollment: definition and effects of enrichment and dose in trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in neuropathic pain. A systematic review. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2008;66(2):266‐75. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03200.x] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Straube 2010
Sultan 2008
Torrance 2006
Tracey 2011
-
- Tracey I. Can neuroimaging studies identify pain endophenotypes in humans?. Nature Reviews Neurology 2011;7(3):173‐81. [doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2011.4] - PubMed
Treede 2008
van Hecke 2014
Vo 2009
von Hehn 2012
Vos 2012
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380(9859):2163‐96. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources