Toward robotically assisted membrane peeling with 3-DOF distal force sensing in retinal microsurgery
- PMID: 25571572
- PMCID: PMC4289593
- DOI: 10.1109/EMBC.2014.6945204
Toward robotically assisted membrane peeling with 3-DOF distal force sensing in retinal microsurgery
Abstract
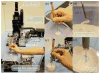
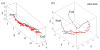
Retinal microsurgery requires steady and precise manipulation of delicate eye tissues in a very small space. Physiological hand tremor and lack of force sensing are among the main technical challenges, limiting surgical performance. We present a system that consists of the cooperatively controlled Steady-Hand Eye Robot and a miniaturized 3-DOF force sensing instrument to address these limitations. While the robot can effectively suppress hand tremor, enable steady and precise tissue manipulation, the force sensing instrument can provide three dimensional force measurements at the tool tip with submillinewton resolution. Auditory sensory substitution is used to give the user real time force information. Evaluation experiments are conducted using artificial and biological membrane peeling phantoms. Experimental results show that the robotic assistance and force-to-audio sensory substitution can effectively control the magnitude of the tool-to-tissue force. The direction profiles of the membrane peeling forces reflect the different delaminating strategies for different membrane phantoms.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human eye phantom for developing computer and robot-assisted epiretinal membrane peeling.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014:6864-7. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2014.6945205. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014. PMID: 25571573 Free PMC article.
-
Micro-force sensing in robot assisted membrane peeling for vitreoretinal surgery.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2010;13(Pt 3):303-10. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-15711-0_38. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2010. PMID: 20879413 Free PMC article.
-
Force sensing micro-forceps for robot assisted retinal surgery.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012;2012:1401-4. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346201. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012. PMID: 23366162 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid position/force control of an active handheld micromanipulator for membrane peeling.Int J Med Robot. 2016 Mar;12(1):85-95. doi: 10.1002/rcs.1659. Epub 2015 May 11. Int J Med Robot. 2016. PMID: 25962836 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted tremor control for performance enhancement of retinal microsurgeons.Br J Ophthalmol. 2019 Aug;103(8):1195-1200. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-313318. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30573495 Review.
Cited by
-
Robot-assisted vitreoretinal surgery: current perspectives.Robot Surg. 2018;5:1-11. doi: 10.2147/RSRR.S122301. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Robot Surg. 2018. PMID: 29527537 Free PMC article.
-
Haptic Shared Control Framework with Interaction Force Constraint Based on Control Barrier Function for Teleoperation.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 11;25(2):405. doi: 10.3390/s25020405. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39860775 Free PMC article.
-
A concentric tube-based 4-DOF puncturing needle with a novel miniaturized actuation system for vitrectomy.Biomed Eng Online. 2019 Apr 18;18(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12938-019-0666-x. Biomed Eng Online. 2019. PMID: 30999918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilkins JR, Puliafito CA, Hee MR, Duker JS, Reichel E, Coker JG, Schuman JS, Swanson EA, Fujimoto JG. Characterization of epiretinal membranes using optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 1996;103(12):2142–2151. - PubMed
-
- Almony A, Nudleman E, Shah GK, Blinder KJ, Eliott DB, Mittra RA, Tewari A. Techniques, rationale, and outcomes of internal limiting membrane peeling. Retina (Philadelphia, Pa) 2012 May;32(5):877–891. - PubMed
-
- Singhy S, Riviere C. Physiological tremor amplitude during retinal microsurgery. IEEE Northeast Bioengineering Conference. IEEE; 2002; pp. 171–172.
-
- Gupta P, Jensen P, de Juan E. Surgical forces and tactile perception during retinal microsurgery. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. 1999;1679:1218–1225.
-
- He X, Roppenecker D, Gierlach D, Balicki M, Olds K, Gehlbach P, Handa J, Taylor R, Iordachita I. Toward Clinically Applicable Steady-Hand Eye Robot for Vitreoretinal Surgery. ASME 2012 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition; 2012; pp. 145–153.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
