Effect of Melilotus suaveolens extract on pulmonary microvascular permeability by downregulating vascular endothelial growth factor expression in rats with sepsis
- PMID: 25571852
- PMCID: PMC4368078
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3146
Effect of Melilotus suaveolens extract on pulmonary microvascular permeability by downregulating vascular endothelial growth factor expression in rats with sepsis
Abstract
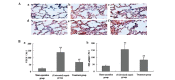
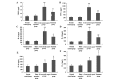
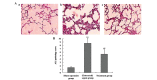
A typical indicator of sepsis is the development of progressive subcutaneous and body‑cavity edema, which is caused by the breakdown of endothelial barrier function, leading to a marked increase in vascular permeability. Microvascular leakage predisposes to microvascular thrombosis, breakdown of microcirculatory flow and organ failure, which are common events preceding mortality in patients with severe sepsis. Melilotus suaveolens (M. suaveolens) is a Traditional Tibetan Medicine. Previous pharmacological studies have demonstrated that an ethanolic extract of M. suaveolens has powerful anti‑inflammatory activity and leads to an improvement in capillary permeability. However, the mechanisms underlying its pharmacological activity remain elusive. The present study aimed to assess the impact of M. suaveolens extract tablets on pulmonary vascular permeability, and their effect on regulating lung inflammation and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the lung tissue of rats with sepsis. A cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) sepsis model was established for both the control and treatment groups. ~2 h prior to surgery, 25 mg/kg of M. suaveolens extract tablet was administered to the treatment group. Polymerase chain reaction and western blot analyses were used to assess the expression of nuclear factor (NF)‑κB and VEGF in the lung tissue, and ELISA was applied to detect changes in serum tumor necrosis factor‑α as well as interleukins (IL) ‑1, ‑4, ‑6, and ‑10. The lung permeability, wet/dry weight ratio and lung pathology were determined. The results demonstrated that in the lung tissue of CLP‑rats with sepsis, M. suaveolens extract inhibited the expression of NF‑κB, reduced the inflammatory response and blocked the expression of VEGF, and thus significantly decreased lung microvascular permeability. The effects of M. Suaveolens extract may be of potential use in the treatment of CLP‑mediated lung microvascular permeability.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of Melilotus extract on lung injury via the upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein-8-like 2 in septic mice.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Mar;11(3):1675-84. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2965. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25405912 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of melilotus extract on lung injury by upregulating the expression of cannabinoid CB2 receptors in septic rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Mar 11;14:94. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-94. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24612782 Free PMC article.
-
Penehyclidine hydrochloride decreases pulmonary microvascular permeability by upregulating beta arrestins in a murine cecal ligation and puncture model.J Surg Res. 2015 Jan;193(1):391-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.07.002. Epub 2014 Jul 5. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25096356
-
Novel therapies for microvascular permeability in sepsis.Curr Drug Targets. 2007 Apr;8(4):509-14. doi: 10.2174/138945007780362719. Curr Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17430121 Review.
-
Microvascular dysfunction in sepsis.Microcirculation. 2000 Apr;7(2):83-101. doi: 10.1038/sj.mn.7300096. Microcirculation. 2000. PMID: 10802851 Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulated miRNAs Targeting Adiponectin Signaling in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 25;26(15):7196. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157196. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of thrombosis on pulmonary endothelial injury and repair following sepsis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;312(4):L441-L451. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00441.2016. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28130261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights into Sepsis Therapy Using Sepia Officinalis.Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2016 Jan 2;9(1):e29331. doi: 10.5812/jjm.29331. eCollection 2016 Jan. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27099690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park SJ, Pai KS, Kim JH, Shin JI. What dose of intravenous immunoglobulin should be administered in Kawasaki disease with suspected systemic capillary leak syndrome? Comment on: shock: an unusual presentation of Kawasaki disease (Eur J Pediatr 2011 Jul; 170(7):941–3) Eur J Pediatr. 2012;17:203–204. doi: 10.1007/s00431-011-1602-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

