Gradient-based delineation of the primary GTV on FLT PET in squamous cell cancer of the thoracic esophagus and impact on radiotherapy planning
- PMID: 25572431
- PMCID: PMC4331414
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-014-0304-5
Gradient-based delineation of the primary GTV on FLT PET in squamous cell cancer of the thoracic esophagus and impact on radiotherapy planning
Abstract
Background: To validate a gradient-based segmentation method for gross tumor volume(GTV) delineation on (8)F-fluorothymidine (FLT)positron emission tomography (PET)/ computer tomography (CT) in esophageal squamous cell cancer through pathologic specimen, in comparison with standardized uptake values (SUV) threshold-based methods and CT. The corresponding impact of this GTV delineation method on treatment planning was evaluated.
Methods and materials: Ten patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer were enrolled. Before radical surgery, all patients underwent FLT-PET/CT. GTVs were delineated by using four methods. GTVGRAD, GTV1.4 and GTV30%max were segmented on FLT PET using a gradient-based method, a fixed threshold of 1.4 SUV and 30% of SUVmax, respectively. GTVCT was based on CT data alone. The maximum longitudinal tumor length of each segmented GTV was compared with the measured tumor length of the pathologic gross tumor length (LPath). GTVGRAD, GTV1.4 and GTV30%max were compared with GTVCT by overlap index. Two radiotherapy plannings (planGRAD) and (planCT) were designed for each patient based on GTVGRAD and GTVCT. The dose-volume parameters for target volume and normal tissues, CI and HI of planGRAD and planCT were compared.
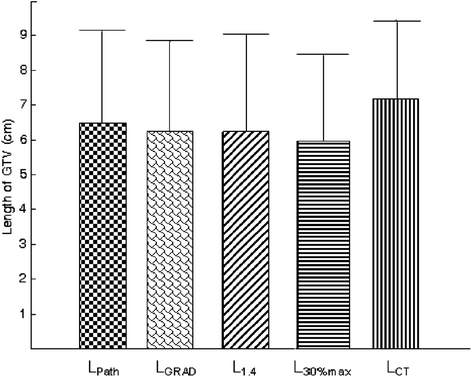
Results: The mean ± standard deviation of LPath was 6.47 ± 2.70 cm. The mean ± standard deviation of LGRAD,L1.4, L30%max and LCT were 6.22 ± 2.61, 6.23 ± 2.80, 5.95 ± 2.50,7.17 ± 2.28 cm, respectively. The Pearson correlation coefficients between LPath and each segmentation method were 0.989, 0.920, 0.920 and 0.862, respectively. The overlap indices of GTVGRAD, GTV1.4, GTV30%max when compared with GTVCT were 0.75 ± 0.12, 0.71 ± 0.12, 0.57 ± 0.10, respectively. The V5, V10, V20, V30 and mean dose of total-lung,V30 and mean dose of heart of planGRAD were significantly lower than planCT.
Conclusions: The gradient-based method provided the closest estimation of target length. The radiotherapy plannings based on the gradient-based segmentation method reduced the irradiated volume of lung, heart in comparison to CT.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of (18)F-fluorothymidine and (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT in delineating gross tumor volume by optimal threshold in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of thoracic esophagus.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010 Mar 15;76(4):1235-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1681. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010. PMID: 19910143
-
GTV spatial conformity between different delineation methods by 18FDG PET/CT and pathology in esophageal cancer.Radiother Oncol. 2009 Dec;93(3):441-6. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2009.07.003. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Radiother Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19682760
-
Using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography to estimate the length of gross tumor in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009 Jan 1;73(1):136-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.04.015. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. PMID: 18538492
-
Positron emission tomography for radiation treatment planning.Strahlenther Onkol. 2005 Aug;181(8):483-99. doi: 10.1007/s00066-005-1422-7. Strahlenther Onkol. 2005. PMID: 16044216 Review.
-
Usefulness of four dimensional (4D) PET/CT imaging in the evaluation of thoracic lesions and in radiotherapy planning: Review of the literature.Lung Cancer. 2016 Jun;96:78-86. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.03.019. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27133755 Review.
Cited by
-
The Prognostic Value of Pretreatment Gallium-68 DOTATATE Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Irradiated Non-benign Meningioma.Indian J Nucl Med. 2019 Oct-Dec;34(4):278-283. doi: 10.4103/ijnm.IJNM_98_19. Indian J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 31579356 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy volume delineation using 18F-FDG-PET/CT modifies gross node volume in patients with oesophageal cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2018 Nov;20(11):1460-1466. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1879-3. Epub 2018 May 2. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29721766
-
Clinico-pathological factors and [18F]FDG PET/CT metabolic parameters for prediction of progression-free survival in radioiodine refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Dec 20;24(1):344. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01525-9. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39707210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janssen MH, Ollers MC, Riedl RG, van den Bogaard J, Buijsen J, van Stiphout RG, Aerts HJ, Lambin P, Lammering G. Accurate prediction of pathological rectal tumor response after two weeks of preoperative radiochemotherapy using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography-computed tomography imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77:392–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.04.030. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vesselle H, Grierson J, Muzi M, Pugsley JM, Schmidt RA, Rabinowitz P, Peterson LM, Vallières E, Wood DE. In vivo validationof 3′deoxy-3′-[18F] fluorothymidine ([18F]FLT) as a proliferation imaging tracer in humans: correlation of [18F]FLT uptake by positron emission tomography with Ki-67 immunohisto- chemistry and flow cytometry in human lung tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:3315–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

