Mutational profiling of therapy-related myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia by next generation sequencing, a comparison with de novo diseases
- PMID: 25573287
- PMCID: PMC5548131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2014.12.006
Mutational profiling of therapy-related myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia by next generation sequencing, a comparison with de novo diseases
Abstract
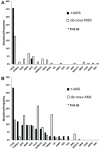
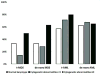
In this study we used a next generation sequencing-based approach to profile gene mutations in therapy-related myelodysplastic syndromes (t-MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (t-AML); and compared these findings with de novo MDS/AML. Consecutive bone marrow samples of 498 patients, including 70 therapy-related (28 MDS and 42 AML) and 428 de novo (147 MDS and 281 AML) were analyzed using a modified-TruSeq Amplicon Cancer Panel (Illumina) covering mutation hotspots of 53 genes. Overall, mutation(s) were detected in 58.6% of t-MDS/AML and 56.8% of de novo MDS/AML. Of therapy-related cases, mutations were detected in 71.4% of t-AML versus 39.3% t-MDS (p=0.0127). TP53 was the most common mutated gene in t-MDS (35.7%) as well as t-AML (33.3%), significantly higher than de novo MDS (17.7%) (p=0.0410) and de novo AML (12.8%) (p=0.0020). t-AML showed more frequent PTPN11 but less NPM1 and FLT3 mutations than de novo AML. In summary, t-MDS/AML shows a mutation profile different from their de novo counterparts. TP53 mutations are highly and similarly prevalent in t-MDS and t-AML but mutations in genes other than TP53 were more frequent in t-AML than t-MDS. The molecular genetic profiling further expands our understanding in this group of clinically aggressive yet heterogeneous myeloid neoplasms.
Keywords: AML; Karyotype; MDS; Next generation sequencing; TP53; Therapy-related.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors do not report conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Vardiman JW, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Larson RA, Matutes E, Baumann I, et al. Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris L, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al., editors. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC); 2008. pp. 127–9.
-
- Greco M, D’Alo F, Scardocci A, Criscuolo M, Fabiani E, Guidi F, et al. Promoter methylation of DAPK1, E-cadherin and thrombospondin-1 in de novo and therapy-related myeloid neoplasms. Blood cells, molecules & diseases. 2010;45:181–5. - PubMed
-
- Voso MT, D’Alo F, Greco M, Fabiani E, Criscuolo M, Migliara G, et al. Epigenetic changes in therapy-related MDS/AML. Chemico-biological interactions. 2010;184:46–9. - PubMed
-
- Olney HJ, Le Beau MM. The cytogenetics of myelodysplastic syndromes. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2001;14:479–95. - PubMed
-
- Smith SM, Le Beau MM, Huo D, Karrison T, Sobecks RM, Anastasi J, et al. Clinical-cytogenetic associations in 306 patients with therapy-related myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia: the University of Chicago series. Blood. 2003;102:43–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

