Tiotropium and olodaterol fixed-dose combination versus mono-components in COPD (GOLD 2-4)
- PMID: 25573406
- PMCID: PMC4391658
- DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00136014
Tiotropium and olodaterol fixed-dose combination versus mono-components in COPD (GOLD 2-4)
Erratum in
-
Author correction. Tiotropium and olodaterol fixed-dose combination versus mono-components in COPD (GOLD 2-4).Eur Respir J. 2015 Jun;45(6):1763. doi: 10.1183/09031936.50136014. Eur Respir J. 2015. PMID: 26028626 Free PMC article.
Abstract
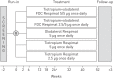
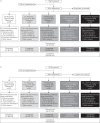
Efficacy and safety of tiotropium+olodaterol fixed-dose combination (FDC) compared with the mono-components was evaluated in patients with moderate to very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in two replicate, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre, phase III trials. Patients received tiotropium+olodaterol FDC 2.5/5 μg or 5/5 μg, tiotropium 2.5 μg or 5 μg, or olodaterol 5 μg delivered once-daily via Respimat inhaler over 52 weeks. Primary end points were forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) area under the curve from 0 to 3 h (AUC0-3) response, trough FEV1 response and St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score at 24 weeks. In total, 5162 patients (2624 in Study 1237.5 and 2538 in Study 1237.6) received treatment. Both FDCs significantly improved FEV1 AUC0-3 and trough FEV1 response versus the mono-components in both studies. Statistically significant improvements in SGRQ total score versus the mono-components were only seen for tiotropium+olodaterol FDC 5/5 μg. Incidence of adverse events was comparable between the FDCs and the mono-components. These studies demonstrated significant improvements in lung function and health-related quality of life with once-daily tiotropium+olodaterol FDC versus mono-components over 1 year in patients with moderate to very severe COPD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01431274 NCT01431287.
Copyright ©ERS 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Disclosures can be found alongside the online version of this article at
Figures

Comment in
-
Treatment of COPD and the TOnado trial: a tempest in a teapot?Eur Respir J. 2015 Apr;45(4):869-71. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00027915. Eur Respir J. 2015. PMID: 25829428 No abstract available.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Updated 2014. www.goldcopd.org/uploads/users/files/GOLD_Report2014_Feb07.pdf Date last updated: 2014. Date last accessed: 2 June 2014. - PubMed
-
- Tashkin DP, Celli B, Senn S, et al. , for the UPLIFT Study Investigators. A 4-year trial of tiotropium in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1543–1554. - PubMed
-
- Bateman ED, Tashkin D, Siafakas N, et al. . A one-year trial of tiotropium Respimat® plus usual therapy in COPD patients. Respir Med 2010; 104: 1460–1472. - PubMed
-
- Cooper CB, Celli BR, Jardim JR, et al. . Treadmill endurance during 2-year treatment with tiotropium in patients with COPD: a randomized trial. Chest 2013; 144: 490–497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
