Protective effect of the combinations of glycyrrhizic, ferulic and cinnamic acid pretreatment on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats
- PMID: 25574212
- PMCID: PMC4280987
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.2134
Protective effect of the combinations of glycyrrhizic, ferulic and cinnamic acid pretreatment on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats
Abstract
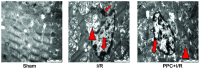
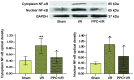
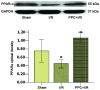
The aim of this study was to find an effective drug cocktail pretreatment to protect myocardial tissue of the heart from ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. The mechanisms underlying the effects of the drug cocktail were subsequently explored in order to expand the application of Dang-gui-si-ni-tang (DGSN), a Traditional Chinese Medicine. The active components of DGSN in the serum following oral administration were investigated using high-performance liquid chromatography. The activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were then analyzed to show the effect of the active components in the treatment of myocardial I/R injury. An L16 (44) orthogonal experiment was utilized to determine the most effective cocktail mix and the mechanism underlying the effect of this mix on myocardial I/R injury was investigated. It was observed that FCG, a mixture of glycyrrhizic (50 mg/kg), cinnamic (200 mg/kg) and ferulic (300 mg/kg) acid, was the optimal drug cocktail present in DGSN. This was absorbed into the blood following oral administration and was shown to decrease MDA levels and increase the activity of SOD. In conclusion, the findings suggest that FCG, a combination of active ingredients in the DGSN decoction, can be absorbed into the blood and protect the myocardium from I/R injury.
Keywords: cinnamic acid; ferulic acid; glycyrrhizic acid; ischemia-reperfusion cocktail.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Discovery of potential pharmacodynamic ingredients of Dang-Gui-Si-Ni decoction based on absorbed ingredients and molecular docking.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jul 15;275:114045. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114045. Epub 2021 Apr 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33831463
-
Effect on eNOS/NO Pathway in MIRI rats with preconditioning of GFPC from Dang Gui Si Ni decoction.Pharmacognosy Res. 2014 Apr;6(2):133-7. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.129032. Pharmacognosy Res. 2014. PMID: 24761117 Free PMC article.
-
Shenxian-Shengmai Oral Liquid Reduces Myocardial Oxidative Stress and Protects Myocardium from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(6):2503-2516. doi: 10.1159/000492688. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30121659
-
Fingerprint analysis of dang-gui-Si-Ni decoction and its anticoagulant activity in vivo-in vitro.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 May 10;325:117890. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117890. Epub 2024 Feb 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38336186
-
Protective effect of Sheng-Nao-Kang decoction on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):228-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.015. Epub 2013 Oct 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24161430
Cited by
-
Shenxiang Suhe pill improves cardiac function through modulating gut microbiota and serum metabolites in rats after acute myocardial infarction.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):1-12. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2289577. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 38084911 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen protects against myocardial reperfusion injury via the inhibition of inflammation and the modulation of autophagy.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 4;8(67):111522-111534. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22869. eCollection 2017 Dec 19. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29340072 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Diammonium Glycyrrhizinate in Improving Focal Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats Through Multiple Mechanisms.Dose Response. 2022 Dec 1;20(4):15593258221142792. doi: 10.1177/15593258221142792. eCollection 2022 Oct-Dec. Dose Response. 2022. PMID: 36479318 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a tri-drug treatment against lung cancer using orthogonal design in preclinical studies.PeerJ. 2023 Jul 10;11:e15672. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15672. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37456863 Free PMC article.
-
Ferulic Acid against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Heart Toxicity in Mice by Inhibiting NF-κB Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:1261270. doi: 10.1155/2016/1261270. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 26881001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tissier R, Cohen MV, Downey JM. Protecting the acutely ischemic myocardium beyond reperfusion therapies: are we any closer to realizing the dream of infarct size elimination? Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2007;100:794–802. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
