Terahertz spectroscopic imaging and properties of gastrointestinal tract in a rat model
- PMID: 25574429
- PMCID: PMC4285596
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.5.004162
Terahertz spectroscopic imaging and properties of gastrointestinal tract in a rat model
Abstract
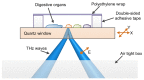
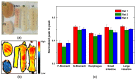
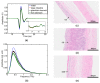
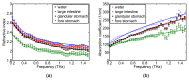
We have investigated basic properties of normal gastrointestinal (GI) tract tissues, including glandular stomach (GS), fore stomach (FS), large intestine (LI), small intestine (SI), and esophagus (ESO), from a rat model using terahertz (THz) reflection imaging and spectroscopy. The THz images collected from stratified squamous epithelia (SSE) of FS and ESO show a lower peak-to-peak value compared to those from columnar epithelia (CE) of GS, LI, or SI because the SSE contains less water than CE. The refractive index and absorption coefficient of FS were less than those of GS or LI, both having values similar to those of water. Additionally, we report internal reflection THz signals from ESO, although we were unable to determine the exact interface for this internal reflection.
Keywords: (170.3880) Medical and biological imaging; (170.6510) Spectroscopy, tissue diagnostics; (170.6795) Terahertz imaging; (300.6495) Spectroscopy, terahertz.
Figures
References
-
- Markelz A. G., Roitberg A., Heilweil E. J., “Pulsed terahertz spectroscopy of DNA, bovine serum albumin and collagen between 0.1 and 2.0 THz,” Chem. Phys. Lett. 320(1-2), 42–48 (2000).10.1016/S0009-2614(00)00227-X - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
