Evaluation of 3 dental unit waterline contamination testing methods
- PMID: 25574718
- PMCID: PMC4450747
Evaluation of 3 dental unit waterline contamination testing methods
Abstract
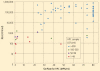
Previous studies have found inconsistent results from testing methods used to measure heterotrophic plate count (HPC) bacteria in dental unit waterline (DUWL) samples. This study used 63 samples to compare the results obtained from an in-office chairside method and 2 currently used commercial laboratory HPC methods (Standard Methods 9215C and 9215E). The results suggest that the Standard Method 9215E is not suitable for application to DUWL quality monitoring, due to the detection of limited numbers of heterotrophic organisms at the required 35°C incubation temperature. The results also confirm that while the in-office chairside method is useful for DUWL quality monitoring, the Standard Method 9215C provided the most accurate results.
Figures
References
-
- Mills SE. The dental unit waterline controversy: defusing the myths, defining the solutions. J Am Dent Assoc. 2000;131(10):1427–1441. - PubMed
-
- Szymanska J. Bacterial contamination of water in dental unit reservoirs. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2007;14(1):137–140. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham AB, Lennox JE, Ross RJ, editors. [Accessed November 7, 2014];Biofilm growth and development. Biofilms: The Hypertextbook. Available at: http://www.biofilmbook.com.
-
- Kohn WG, Collins AS, Cleveland JL, et al. Guidelines for infection control in dental health-care settings – 2003. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2003;52(RR17):1–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
