Laparoscopic treatment of intussusception
- PMID: 25574769
- PMCID: PMC4336417
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2014.10.085
Laparoscopic treatment of intussusception
Abstract
Introduction: The success of laparoscopic approach in children has encouraged the application of this technique in young (<2 years) children with non-complicated intussusception.
Material and method: A retrospective analysis of our database provided a total of 4 patients who underwent laparoscopic reduction of intestinal intussusception between 8/2008 and 4/2013. A comprehensive review of each case was done including the video description of the laparoscopic technique of one of them.
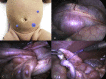
Results: Four patients (2 boys) were treated by laparoscopy for intestinal intussusception. Mean age was 9 months (5-20 months). Delay time between initial symptoms and diagnosis and between diagnosis and surgery were 3.5 days and 6h respectively. Mean operative time was 35min. There were no conversions. There were no complications. Patients were discharged after 2.5 days (2-4 days). We herein report (video) the laparoscopic approach in a 5 month male child who suffered from a ileocecal intussusception. A 10mm trocar was placed in the left lower quadrant and two 5mm trocars were placed in the upper left quadrant and suprapubic just to the right midline. The cause of the intussusception was identified and the bowel was reduced. A concomitant appendectomy was performed.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic reduction of intussusception appears to be a safe procedure, in young children with uncomplicated intussusception.
Keywords: Intussusception; Laparoscopic; Treatment.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic approach for managing intussusception in children: Analysis of 65 cases.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Jan 21;10(3):830-839. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.830. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 35127899 Free PMC article.
-
Mini-laparoscopic reduction of intussusception for children.J Formos Med Assoc. 2000 Jun;99(6):510-2. J Formos Med Assoc. 2000. PMID: 10925560
-
Laparoscopic-assisted pneumatic reduction of intussusception.J Pediatr Surg. 1997 Aug;32(8):1147-8. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(97)90671-0. J Pediatr Surg. 1997. PMID: 9269959
-
Laparoscopic versus open reduction of intussusception in children: a retrospective review and meta-analysis.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2014 Jul;24(7):518-22. doi: 10.1089/lap.2013.0415. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2014. PMID: 24987845 Review.
-
Single-incision assisted laparoscopic surgery (SILS) in the treatment of an intussusception induced by a solitary hamartomatous polyp: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2015 Jun 2;9:125. doi: 10.1186/s13256-015-0606-8. J Med Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 26031291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Management of intussusception in children: A systematic review.J Pediatr Surg. 2021 Mar;56(3):587-596. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2020.09.055. Epub 2020 Oct 6. J Pediatr Surg. 2021. PMID: 33158508 Free PMC article.
-
Management of intussusception in children: A comparative study of hydrostatic reduction with saline under ultrasound guidance versus laparoscopic assistance.Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2023 Jul-Sep;20(3):171-175. doi: 10.4103/ajps.ajps_20_22. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2023. PMID: 37470551 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic approach for managing intussusception in children: Analysis of 65 cases.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Jan 21;10(3):830-839. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.830. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 35127899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hill S.J., Koontz C.S., Langness S.M., Wulkan M.L. Laparoscopic versus open reduction of intussusception in children: experience over a decade. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2013;23:166–169. - PubMed
-
- Miller G., Bowman J., Shrier I., Gordon P.H. Natural history of patients with adhesive small bowel obstruction. Br J Surg. 2000;87:1240–1247. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

