Expression, purification, crystallization, and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of the human adiponectin receptors, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2
- PMID: 25575462
- PMCID: PMC4329188
- DOI: 10.1007/s10969-014-9192-z
Expression, purification, crystallization, and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of the human adiponectin receptors, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2
Abstract
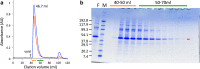
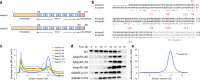
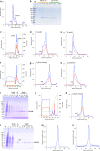
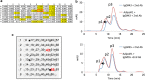
The adiponectin receptors (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2) are membrane proteins with seven transmembrane helices. These receptors regulate glucose and fatty acid metabolism, thereby ameliorating type 2 diabetes. The full-length human AdipoR1 and a series of N-terminally truncated mutants of human AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 were expressed in insect cells. In small-scale size exclusion chromatography, the truncated mutants AdipoR1Δ88 (residues 89-375) and AdipoR2Δ99 (residues 100-386) eluted mostly in the intact monodisperse state, while the others eluted primarily as aggregates. However, gel filtration chromatography of the large-scale preparation of the tag-affinity-purified AdipoR1Δ88 revealed the presence of an excessive amount of the aggregated state over the intact state. Since aggregation due to contaminating nucleic acids may have occurred during the sample concentration step, anion-exchange column chromatography was performed immediately after affinity chromatography, to separate the intact AdipoR1Δ88 from the aggregating species. The separated intact AdipoR1Δ88 did not undergo further aggregation, and was successfully purified to homogeneity by gel filtration chromatography. The purified AdipoR1Δ88 and AdipoR2Δ99 proteins were characterized by thermostability assays with 7-diethylamino-3-(4-maleimidophenyl)-4-methyl coumarin, thin layer chromatography of bound lipids, and surface plasmon resonance analysis of ligand binding, demonstrating their structural integrities. The AdipoR1Δ88 and AdipoR2Δ99 proteins were crystallized with the anti-AdipoR1 monoclonal antibody Fv fragment, by the lipidic mesophase method. X-ray diffraction data sets were obtained at resolutions of 2.8 and 2.4 Å, respectively.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Expression of adiponectin and its receptors in swine.J Anim Sci. 2005 Mar;83(3):565-78. doi: 10.2527/2005.833565x. J Anim Sci. 2005. PMID: 15705753
-
Orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) adiponectin receptors: molecular characterization, mRNA expression, and subcellular location.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014 Mar 1;198:47-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2013.12.013. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24406511
-
Human adiponectin receptor AdipoR1 assumes closed and open structures.Commun Biol. 2020 Aug 14;3(1):446. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01160-4. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 32796916 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of the adiponectin receptors: Differential cell-surface expression and temporal signalling profiles of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 are regulated by the non-conserved N-terminal trunks.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Jul 5;409:121-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25892445
-
Molecular cloning and expression analysis of adiponectin and its receptors (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2) in the hypothalamus of the Huoyan goose during different stages of the egg-laying cycle.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015 Aug 7;13:87. doi: 10.1186/s12958-015-0085-1. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26251033 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Caenorhabditis elegans PAQR-2 and IGLR-2 Protect against Glucose Toxicity by Modulating Membrane Lipid Composition.PLoS Genet. 2016 Apr 15;12(4):e1005982. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005982. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27082444 Free PMC article.
-
Drug development research for novel adiponectin receptor-targeted antidiabetic drugs contributing to healthy longevity.Diabetol Int. 2019 Sep 19;10(4):237-244. doi: 10.1007/s13340-019-00409-6. eCollection 2019 Oct. Diabetol Int. 2019. PMID: 31592400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying antibiotics based on structural differences in the conserved allostery from mitochondrial heme-copper oxidases.Nat Commun. 2022 Dec 8;13(1):7591. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34771-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36481732 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-free synthesis of functional antibody fragments to provide a structural basis for antibody-antigen interaction.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 20;13(2):e0193158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193158. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29462206 Free PMC article.
-
A reproducible and scalable procedure for preparing bacterial extracts for cell-free protein synthesis.J Biochem. 2017 Nov 1;162(5):357-369. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvx039. J Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28992119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, Iwahashi H, Kuriyama H, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Nishida M, Kihara S, Sakai N, Nakajima T, Hasegawa K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20(6):1595–1599. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.20.6.1595. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

