A randomized, double-blind, duloxetine-referenced study comparing efficacy and tolerability of 2 fixed doses of vortioxetine in the acute treatment of adults with MDD
- PMID: 25575488
- PMCID: PMC4432084
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-014-3839-0
A randomized, double-blind, duloxetine-referenced study comparing efficacy and tolerability of 2 fixed doses of vortioxetine in the acute treatment of adults with MDD
Abstract
Rationale: Vortioxetine has reduced depressive symptoms in adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) in multiple clinical trials.
Objectives: The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of vortioxetine 15 and 20 mg vs placebo in adults with MDD.
Methods: Patients were randomized 1:1:1:1 to vortioxetine 15 mg, vortioxetine 20 mg, duloxetine 60 mg (active reference), or placebo. The primary efficacy endpoint was mean change in Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) total score at week 8 (MMRM). Safety/tolerability assessments included physical examinations, vital signs, laboratory evaluations, electrocardiograms, adverse events (AEs), Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale, Arizona Sexual Experiences Scale, and Discontinuation-Emergent Signs and Symptoms checklist.
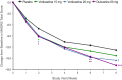
Results: Six hundred and fourteen patients were randomized. Mean changes in MADRS scores were -12.83 (±0.834), -14.30 (±0.890), -15.57 (±0.880), and -16.90 (±0.884) for placebo, vortioxetine 15 mg (P = .224), vortioxetine 20 mg (P = .023), and duloxetine 60 mg (P < .001) (P vs placebo), respectively. AEs reported by ≥5 % of vortioxetine patients included nausea, headache, diarrhea, dizziness, dry mouth, constipation, vomiting, insomnia, fatigue, and upper respiratory infection. Treatment-emergent sexual dysfunction, suicidal ideation or behavior, and discontinuation symptoms were not significantly different between vortioxetine and placebo.
Conclusions: Vortioxetine 20 mg significantly reduced MADRS total scores after 8 weeks of treatment. Both vortioxetine doses were well tolerated.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01153009; www.clinicaltrials.gov/ .
Figures
References
-
- Baldwin DS, Loft H, Dragheim M. A randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled, duloxetine-referenced, fixed-dose study of three dosages of Lu AA21004 in acute treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012;22:482–491. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2011.11.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bang-Andersen B, Ruhland T, Jørgensen M, Smith G, Frederiksen K, Jensen KG, Zhnog H, Nielsen SM, Hogg S, Mørk A, Stensbøl TB. Discovery of 1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl)phenyl]piperazine (Lu AA21004): a novel multimodal compound for the treatment of major depressive disorder. J Med Chem. 2011;54:3206–3221. doi: 10.1021/jm101459g. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

