Syndecan-4 is a major syndecan in primary human endothelial cells in vitro, modulated by inflammatory stimuli and involved in wound healing
- PMID: 25575567
- PMCID: PMC4374057
- DOI: 10.1369/0022155415568995
Syndecan-4 is a major syndecan in primary human endothelial cells in vitro, modulated by inflammatory stimuli and involved in wound healing
Abstract
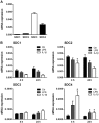
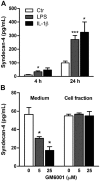
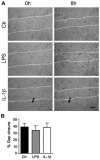
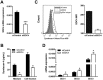
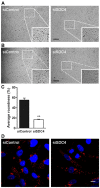
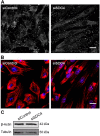
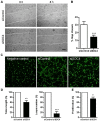
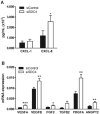
Syndecans are important cell surface proteoglycans with many functions; yet, they have not been studied to a very large extent in primary human endothelial cells. The purpose of this study was to investigate syndecan-4 expression in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and assess its role in inflammatory reactions and experimental wound healing. qRT-PCR analysis revealed that syndecan-3 and syndecan-4 were highly expressed in HUVECs, whereas the expression of syndecan-1 and -2 was low. HUVECs were cultured with the inflammatory mediators lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interleukin 1β (IL-1β). As a result, syndecan-4 expression showed a rapid and strong increase. Syndecan-1 and -2 expressions decreased, whereas syndecan-3 was unaffected. Knockdown of syndecan-4 using siRNA resulted in changes in cellular morphology and focal adhesion sites, delayed wound healing and tube formation, and increased secretion of the pro-inflammatory and angiogenic chemokine, CXCL8. These data suggest functions for syndecan-4 in inflammatory reactions, wound healing and angiogenesis in primary human endothelial cells.
Keywords: angiogenesis; inflammation; primary human endothelial cells; shedding; syndecan-4; wound healing.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Alexopoulou AN, Multhaupt HA, Couchman JR. (2007). Syndecans in wound healing, inflammation and vascular biology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:505-28. - PubMed
-
- Bernfield M, Gotte M, Park PW, Reizes O, Fitzgerald ML, Lincecum J, Zako M. (1999). Functions of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Biochem 68:729-77. - PubMed
-
- Bernfield M, Kokenyesi R, Kato M, Hinkes MT, Spring J, Gallo RL, Lose EJ. (1992). Biology of the syndecans: a family of transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Biol 8:365-93. - PubMed
-
- Chalkiadaki G, Nikitovic D, Berdiaki A, Sifaki M, Krasagakis K, Katonis P, Karamanos NK, Tzanakakis GN. (2009). Fibroblast growth factor-2 modulates melanoma adhesion and migration through a syndecan-4-dependent mechanism. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:1323-1331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

