miR-30 promotes thermogenesis and the development of beige fat by targeting RIP140
- PMID: 25576051
- PMCID: PMC4876748
- DOI: 10.2337/db14-1117
miR-30 promotes thermogenesis and the development of beige fat by targeting RIP140
Abstract
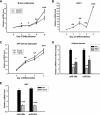
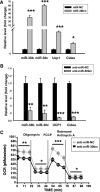
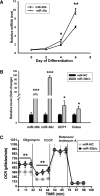
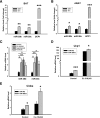
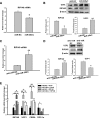
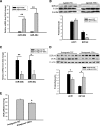
Members of the microRNA (miR)-30 family have been reported to promote adipogenesis and inhibit osteogenesis, yet their role in the regulation of thermogenesis remains unknown. In this study, we show that miR-30b/c concentrations are greatly increased during adipocyte differentiation and are stimulated by cold exposure or the β-adrenergic receptor activator. Overexpression and knockdown of miR-30b and -30c induced and suppressed, respectively, the expression of thermogenic genes such as UCP1 and Cidea in brown adipocytes. Forced expression of miR-30b/c also significantly increased thermogenic gene expression and mitochondrial respiration in primary adipocytes derived from subcutaneous white adipose tissue, demonstrating a promoting effect of miRNAs on the development of beige fat. In addition, knockdown of miR-30b/c repressed UCP1 expression in brown adipose tissue in vivo. miR-30b/c targets the 3'-untranslated region of the receptor-interacting protein 140 (RIP140), and overexpression of miR-30b/c significantly reduced RIP140 expression. Consistent with RIP140 as a target of miR-30b/c in regulating thermogenic gene expression, overexpression of RIP140 greatly suppressed the promoting effect of miR-30b/c on the expression of UCP1 and Cidea in brown adipocytes. Taken together, the data from our study identify miR-30b/c as a key regulator of thermogenesis and uncover a new mechanism underlying the regulation of brown adipose tissue function and the development of beige fat.
© 2015 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Obesity-Associated miR-199a/214 Cluster Inhibits Adipose Browning via PRDM16-PGC-1α Transcriptional Network.Diabetes. 2018 Dec;67(12):2585-2600. doi: 10.2337/db18-0626. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 30279164
-
MiR-27 orchestrates the transcriptional regulation of brown adipogenesis.Metabolism. 2014 Feb;63(2):272-82. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24238035
-
Eicosapentaenoic Acid Potentiates Brown Thermogenesis through FFAR4-dependent Up-regulation of miR-30b and miR-378.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 23;291(39):20551-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.721480. Epub 2016 Aug 3. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27489163 Free PMC article.
-
Meaningful respirometric measurements of UCP1-mediated thermogenesis.Biochimie. 2017 Mar;134:56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.12.005. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 27986537 Review.
-
[Evaluation of Naturally Occurring Compounds Regulating Brown/Beige Adipocyte Differentiation].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(6):861-866. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00173-3. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 31155526 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
A computational biology approach of a genome-wide screen connected miRNAs to obesity and type 2 diabetes.Mol Metab. 2018 May;11:145-159. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Mol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29605715 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative mRNA-microRNA analyses reveal novel interactions related to insulin sensitivity in human adipose tissue.Physiol Genomics. 2016 Feb;48(2):145-53. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00071.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Physiol Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26672043 Free PMC article.
-
The miRNA Interactome in Metabolic Homeostasis.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Dec;26(12):733-745. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26492831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Maternal Diet and Lactation Time on the Exosomal miRNA Cargo in Breast Milk.Foods. 2025 Mar 16;14(6):1003. doi: 10.3390/foods14061003. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40232032 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics profiling reveals microRNA-mediated insulin signaling networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Sep 17;21(Suppl 13):389. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03678-0. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32938376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lowell BB, S-Susulic V, Hamann A, et al. . Development of obesity in transgenic mice after genetic ablation of brown adipose tissue. Nature 1993;366:740–742 - PubMed
-
- Feldmann HM, Golozoubova V, Cannon B, Nedergaard J. UCP1 ablation induces obesity and abolishes diet-induced thermogenesis in mice exempt from thermal stress by living at thermoneutrality. Cell Metab 2009;9:203–209 - PubMed
-
- Arch JR. beta(3)-Adrenoceptor agonists: potential, pitfalls and progress. Eur J Pharmacol 2002;440:99–107 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

