Quantification of ricin, RCA and comparison of enzymatic activity in 18 Ricinus communis cultivars by isotope dilution mass spectrometry
- PMID: 25576235
- PMCID: PMC5303535
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2015.01.003
Quantification of ricin, RCA and comparison of enzymatic activity in 18 Ricinus communis cultivars by isotope dilution mass spectrometry
Abstract
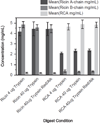
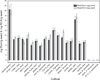
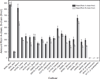
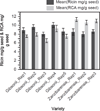
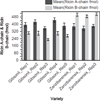
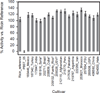
The seeds of the Ricinus communis (Castor bean) plant are the source of the economically important commodity castor oil. Castor seeds also contain the proteins ricin and R. communis agglutinin (RCA), two toxic lectins that are hazardous to human health. Radial immunodiffusion (RID) and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are two antibody-based methods commonly used to quantify ricin and RCA; however, antibodies currently used in these methods cannot distinguish between ricin and RCA due to the high sequence homology of the respective proteins. In this study, a technique combining antibody-based affinity capture with liquid chromatography and multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mass spectrometry (MS) was used to quantify the amounts of ricin and RCA independently in extracts prepared from the seeds of eighteen representative cultivars of R. communis which were propagated under identical conditions. Additionally, liquid chromatography and MRM-MS was used to determine rRNA N-glycosidase activity for each cultivar and the overall activity in these cultivars was compared to a purified ricin standard. Of the cultivars studied, the average ricin content was 9.3 mg/g seed, the average RCA content was 9.9 mg/g seed, and the enzymatic activity agreed with the activity of a purified ricin reference within 35% relative activity.
Keywords: Cultivar; Mass spectrometry; Quantification; RCA; Ricin; Ricinus communis.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allan G, Williams A, Rabinowicz PD, Chan AP, Ravel J, Keim P. Worldwide genotyping of castor bean germplasm (Ricinus communis L.) using AFLPs and SSRs. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2008;55:365–378.
-
- Araki T, Funatsu G. The complete amino acid sequence of the B-chain of ricin E isolated from small-grain castor bean seeds. Ricin E is a gene recombination product of ricin D and Ricinus communis agglutinin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1987;911:191–200. - PubMed
-
- Audi J, Belson M, Patel M, Schier J, Osterloh J. Ricin poisoning a comprehensive review. JAMA. 2005;294:2342–2351. - PubMed
-
- Auld DL, Rolfe RD, McKeon TA. Development of castor with reduced toxicity. J. New Seeds. 2001;3:61–69.
-
- Auld DL, Pinkerton SD, Boroda E, Lombard KA, Murphy CK, Kenworthy KE, Becker WD, Rolfe RD, Ghetie V. Registration of TTU-LRC Castor germplasm with reduced levels of ricin and RCA120. Crop Sci. 2003;43:746–747.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

