Mild hypoxia in vivo regulates cardioprotective SUR2A: A role for Akt and LDH
- PMID: 25576887
- PMCID: PMC4547089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.01.001
Mild hypoxia in vivo regulates cardioprotective SUR2A: A role for Akt and LDH
Abstract
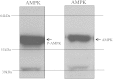
High-altitude residents have lower mortality rates for ischaemic heart disease and this is ascribed to cardiac gene remodelling by chronic hypoxia. SUR2A is a cardioprotective ABC protein serving as a subunit of sarcolemmal ATP-sensitive K(+) channels. The purpose of this study was to determine whether SUR2A is regulated by mild hypoxia in vivo and to elucidate the underlying mechanism. Mice were exposed to either 21% (control) or 18% (mild hypoxia) oxygen for 24h. Exposure to 18% oxygen did not affect partial pressure of O(2) (PO(2)) and CO(2) (PCO(2)) in the blood, haematocrit or level of ATP in the heart. However, hypoxia increased myocardial lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and lactate as well as NAD(+) without affecting total NAD. SUR2A levels were significantly increased as well as myocardial resistance to ischaemia-reperfusion. Exposure to 18% oxygen did not phosphorylate extracellular signal regulated kinases (ERK1/2) or AMP activated protein kinase (AMPK), but it phosphorylated protein kinase B (Akt). An inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K), LY294002 (0.2mg/mouse), abolished all observed effects of hypoxia. LDH inhibitors, galloflavin (50 μM) and sodium oxamate (80 mM) significantly decreased levels of SUR2A in heart embryonic H9c2 cells, while inactive mutant LDH form, gly193-M-LDH increased cellular sensitivity towards stress induced by 2,4-dinitrophenol (10mM). Treatment of H9c2 cells with sodium lactate (30 mM) increased intracellular lactate, but did not affect LDH activity or SUR2A levels. We conclude that PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and LDH play a crucial role in increase of cardiac SUR2A induced by in vivo exposure to 18% oxygen.
Keywords: Akt; Heart; Hypoxia; LDH; Oxygen; SUR2A.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Exposure to 15% oxygen in vivo up-regulates cardioprotective SUR2A without affecting ERK1/2 and AKT: a crucial role for AMPK.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Jul;21(7):1342-1350. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13064. Epub 2017 Jan 25. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28121062 Free PMC article.
-
Shikonin protects H9C2 cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Aug;104:712-717. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.144. Epub 2018 May 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29807220
-
Asperosaponin VI protects cardiac myocytes from hypoxia-induced apoptosis via activation of the PI3K/Akt and CREB pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Dec 15;649(1-3):100-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.08.060. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20863824
-
SUR2A as a base for cardioprotective therapeutic strategies.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):6717-6723. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07281-9. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35301655 Review.
-
Cardioprotective SUR2A promotes stem cell properties of cardiomyocytes.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Oct 12;168(5):5090-2. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.07.182. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23932869 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The involvement of protein kinases in the cardioprotective effect of chronic hypoxia.Physiol Res. 2020 Dec 22;69(6):933-945. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934439. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Physiol Res. 2020. PMID: 33129243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin down-regulates cardioprotective SUR2A in the heart-derived H9c2 cells: A possible explanation for some adverse effects of insulin therapy.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018 Sep 6;16:12-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2018.08.005. eCollection 2018 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018. PMID: 30211323 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to 15% oxygen in vivo up-regulates cardioprotective SUR2A without affecting ERK1/2 and AKT: a crucial role for AMPK.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Jul;21(7):1342-1350. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13064. Epub 2017 Jan 25. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28121062 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics-driven approaches for identifying therapeutic targets in drug discovery.MedComm (2020). 2024 Nov 11;5(11):e792. doi: 10.1002/mco2.792. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39534557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A link between ATP and SUR2A: A novel mechanism explaining cardioprotection at high altitude.Int J Cardiol. 2015;189:73-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.04.069. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Int J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25885875 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Burke M.A., Mutharasan R.K., Ardehali H. The sulfonylurea receptor, an atypical ATP-binding cassette protein, and its regulation of the KATP channel. Circ. Res. 2008;102:164–176. - PubMed
-
- Sudhir R., Sukhodub A., Du Q., Jovanović S., Jovanović A. Ageing-induced decline in physical endurance in mice is associated with decrease in cardiac SUR2A and increase in cardiac susceptibility to metabolic stress: therapeutic prospects for up-regulation of SUR2A. Biogerontology. 2011;12:147–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

