The Galectin-9/Tim-3 pathway is involved in the regulation of NK cell function at the maternal-fetal interface in early pregnancy
- PMID: 25578313
- PMCID: PMC4711677
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2014.126
The Galectin-9/Tim-3 pathway is involved in the regulation of NK cell function at the maternal-fetal interface in early pregnancy
Abstract
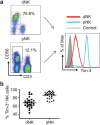
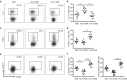
Decidual natural killer (dNK) cells actively participate in the establishment and maintenance of maternal-fetal immune tolerance and act as local guardians against infection. However, how dNK cells maintain the immune balance between tolerance and anti-infection immune responses during pregnancy remains unknown. Here, we demonstrated that the inhibitory molecule T-cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain-containing molecule-3 (Tim-3) are expressed on over 60% of dNK cells. Tim-3(+) dNK cells display higher interleukin (IL)-4 and lower tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and perforin production. Human trophoblast cells can induce the transformation of peripheral NK cells into a dNK-like phenotype via the secretion of galectin-9 (Gal-9) and the interaction between Gal-9 and Tim-3. In addition, trophoblasts inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine and perforin production by dNK cells, which can be attenuated by Tim-3 neutralizing antibodies. Interestingly, a decreased percentage of Tim-3-expressing dNK cells were observed in human miscarriages and murine abortion-prone models. Moreover, T helper (Th)2-type cytokines were decreased and Th1-type cytokines were increased in Tim-3(+) but not Tim-3(-) dNK cells from human and mouse miscarriages. Therefore, our results suggest that the Gal-9/Tim-3 signal is important for the regulation of dNK cell function, which is beneficial for the maintenance of a normal pregnancy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tim-3 Is Upregulated in NK Cells during Early Pregnancy and Inhibits NK Cytotoxicity toward Trophoblast in Galectin-9 Dependent Pathway.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 20;11(1):e0147186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147186. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26789128 Free PMC article.
-
Decidual Natural Killer Cells: A Good Nanny at the Maternal-Fetal Interface During Early Pregnancy.Front Immunol. 2021 May 12;12:663660. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663660. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 (Tim-3) regulate CD4+ T cells to induce Type 2 helper T cell (Th2) bias at the maternal-fetal interface.Hum Reprod. 2016 Apr;31(4):700-11. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew019. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 26908841
-
Galectin-9 Alleviates LPS-Induced Preeclampsia-Like Impairment in Rats via Switching Decidual Macrophage Polarization to M2 Subtype.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 10;9:3142. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03142. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30687334 Free PMC article.
-
Tim-3: Expression on immune cells and roles at the maternal-fetal interface.J Reprod Immunol. 2016 Nov;118:92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2016.10.113. Epub 2016 Oct 20. J Reprod Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27792886 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk Between Trophoblasts and Decidual Immune Cells: The Cornerstone of Maternal-Fetal Immunotolerance.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 25;12:642392. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.642392. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717198 Free PMC article.
-
Tim-3 Is Upregulated in NK Cells during Early Pregnancy and Inhibits NK Cytotoxicity toward Trophoblast in Galectin-9 Dependent Pathway.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 20;11(1):e0147186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147186. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26789128 Free PMC article.
-
TIM-3: a crucial regulator of NK cells in pregnancy.Cell Mol Immunol. 2017 Sep 11;14(11):948-50. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.85. Online ahead of print. Cell Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28890545 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Galectins: Double-edged Swords in the Cross-roads of Pregnancy Complications and Female Reproductive Tract Inflammation and Neoplasia.J Pathol Transl Med. 2015 May;49(3):181-208. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2015.02.25. Epub 2015 May 15. J Pathol Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26018511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decidual Natural Killer Cells: A Good Nanny at the Maternal-Fetal Interface During Early Pregnancy.Front Immunol. 2021 May 12;12:663660. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663660. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- 1Zenclussen AC, Schumacher A, Zenclussen ML, Wafula P, Volk HD. Immunology of pregnancy: cellular mechanisms allowing fetal survival within the maternal uterus. Expert Rev Mol Med 2007; 9: 1–14. - PubMed
-
- 2Erlebacher A. Immunology of the maternal–fetal interface. Annu Rev Immunol 2013; 31: 387–411. - PubMed
-
- 4Krasnow JS, Tollerud DJ, Naus G, DeLoia JA. Endometrial Th2 cytokine expression throughout the menstrual cycle and early pregnancy. Hum Reprod 1996; 11: 1747–1754. - PubMed
-
- 5Tilburgs T, Scherjon SA, Claas FH. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-mediated immune regulation of decidual leukocytes at the fetal–maternal interface. J Reprod Immunol 2010; 85: 58–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

