Heterosynaptic regulation of external globus pallidus inputs to the subthalamic nucleus by the motor cortex
- PMID: 25578364
- PMCID: PMC4304914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.022
Heterosynaptic regulation of external globus pallidus inputs to the subthalamic nucleus by the motor cortex
Abstract
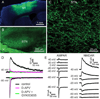
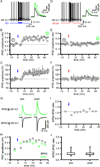
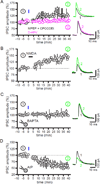
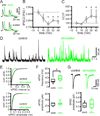
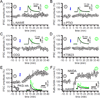
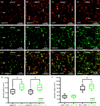
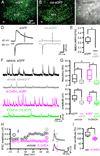
The two principal movement-suppressing pathways of the basal ganglia, the so-called hyperdirect and indirect pathways, interact within the subthalamic nucleus (STN). An appropriate level and pattern of hyperdirect pathway cortical excitation and indirect pathway external globus pallidus (GPe) inhibition of the STN are critical for normal movement and are greatly perturbed in Parkinson's disease. Here we demonstrate that motor cortical inputs to the STN heterosynaptically regulate, through activation of postsynaptic NMDA receptors, the number of functional GABAA receptor-mediated GPe-STN inputs. Therefore, a homeostatic mechanism, intrinsic to the STN, balances cortical excitation by adjusting the strength of GPe inhibition. However, following the loss of dopamine, excessive cortical activation of STN NMDA receptors triggers GPe-STN inputs to strengthen abnormally, contributing to the emergence of pathological, correlated activity.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Striking the right balance: cortical modulation of the subthalamic nucleus-globus pallidus circuit.Neuron. 2015 Jan 21;85(2):233-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.062. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 25611504
-
Interaction between hyperdirect and indirect basal ganglia pathways.Mov Disord. 2015 Jun;30(7):909. doi: 10.1002/mds.26273. Epub 2015 May 28. Mov Disord. 2015. PMID: 26018416 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cortical Control of Subthalamic Neuronal Activity through the Hyperdirect and Indirect Pathways in Monkeys.J Neurosci. 2020 Sep 23;40(39):7451-7463. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0772-20.2020. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32847963 Free PMC article.
-
Striking the right balance: cortical modulation of the subthalamic nucleus-globus pallidus circuit.Neuron. 2015 Jan 21;85(2):233-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.062. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 25611504
-
Interaction between hyperdirect and indirect basal ganglia pathways.Mov Disord. 2015 Jun;30(7):909. doi: 10.1002/mds.26273. Epub 2015 May 28. Mov Disord. 2015. PMID: 26018416 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
GABAergic control of the subthalamic nucleus.Prog Brain Res. 2007;160:173-88. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)60010-1. Prog Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17499114 Review.
-
Globus pallidus external segment.Prog Brain Res. 2007;160:111-33. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)60007-1. Prog Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17499111 Review.
Cited by
-
Cortical Control of Subthalamic Neuronal Activity through the Hyperdirect and Indirect Pathways in Monkeys.J Neurosci. 2020 Sep 23;40(39):7451-7463. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0772-20.2020. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32847963 Free PMC article.
-
Significance and Translational Value of High-Frequency Cortico-Basal Ganglia Oscillations in Parkinson's Disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2019;9(1):183-196. doi: 10.3233/JPD-181480. J Parkinsons Dis. 2019. PMID: 30594935 Free PMC article.
-
Decoupling of interacting neuronal populations by time-shifted stimulation through spike-timing-dependent plasticity.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Feb 1;19(2):e1010853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010853. eCollection 2023 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 36724144 Free PMC article.
-
The dendritic engram.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Jul 27;17:1212139. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1212139. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37576932 Free PMC article.
-
The external globus pallidus: progress and perspectives.Eur J Neurosci. 2016 May;43(10):1239-65. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13196. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Eur J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26841063 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

