Weight loss prior to lung transplantation is associated with improved survival
- PMID: 25578626
- PMCID: PMC4417392
- DOI: 10.1016/j.healun.2014.11.018
Weight loss prior to lung transplantation is associated with improved survival
Abstract
Background: Obesity is associated with increased mortality after lung transplantation and is a relative contraindication to transplant. It is unknown whether weight reduction prior to transplantation ameliorates this risk. Our objective was to determine whether weight loss prior to lung transplantation improves survival.
Methods: Our investigation was a two-center, retrospective cohort study of lung transplant recipients between January 1, 2000 and November 5, 2010. Change in weight, demographics, transplant details, lung allocation score, length of intensive care and mechanical ventilator days and graft and patient survival were abstracted. Wilcoxon's signed-rank test and the Cox proportional hazard model were used for analysis where appropriate.
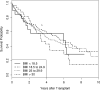
Results: Three hundred fifty-five patients (55% male, median age 59 years) satisfied inclusion and exclusion criteria. After adjusting for standard demographic and clinical measures, a 1-unit reduction in BMI pre-transplant was associated with a reduced risk of death with a hazard ratio 0.89 (95% confidence interval 0.82 to 0.96; p = 0.004). This survival benefit persisted in the group with baseline BMI ≥ 25 kg/m(2) (overweight and obese) and hazard ratio 0.85 (95% CI 0.77 to 0.95; p = 0.003), but not in those with a BMI ≤ 24.9 kg/m(2). The 1-unit reduction in BMI was also associated with a 6.1% decrease in median mechanical ventilator days (p = 0.02) and a trend toward decreased intensive care unit length of stay (p = 0.06).
Conclusions: A reduction in BMI prior to lung transplantation was associated with a reduction in the risk of death and mechanical ventilator days. A greater reduction in BMI was associated with a greater survival benefit.
Keywords: lung transplantation; obesity; patient selection; survival; weight loss.
Copyright © 2015 International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- [May 14, 2014]; Available from: http://www.srtr.org/.
-
- Kanasky WF, Jr., Anton SD, Rodrigue JR, Perri MG, Szwed T, Baz MA. Impact of body weight on long-term survival after lung transplantation. Chest. 2002;121:401–6. - PubMed
-
- Allen JG, Arnaoutakis GJ, Weiss ES, Merlo CA, Conte JV, Shah AS. The impact of recipient body mass index on survival after lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010;29:1026–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical