Management of hemolytic uremic syndrome
- PMID: 25580273
- PMCID: PMC4278190
- DOI: 10.12703/P6-119
Management of hemolytic uremic syndrome
Abstract
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a disease characterized by hemolysis, thrombocytopenia, and acute kidney injury, although other organs may be involved. Most cases are due to infection with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC). Early identification and initiation of best supportive care, with microbiological input to identify the pathogen, result in a favorable outcome in most patients. The remaining 10% of HUS cases are classed together as atypical HUS and have a diverse etiology. The majority are due to inherited or acquired abnormalities that lead to a failure to control complement activation. Atypical HUS occurring in other situations (for example, related to pregnancy or kidney transplantation) may also involve excessive complement activation. Plasma therapies can reverse defective complement control, and it is now possible to specifically target complement activation. This has led to improved outcomes in patients with atypical forms of HUS. We will review our current understanding of the pathogenesis of HUS and how this has led to advances in patient care.
Figures
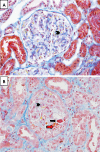
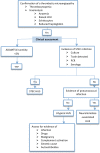

References
-
- Furlan M, Robles R, Solenthaler M, Wassmer M, Sandoz P, Lammle B. Deficient activity of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1997;89:3097–103. - PubMed
-
- Garg AX, Suri RS, Barrowman N, Rehman F, Matsell D, Rosas-Arellano MP, Salvadori M, Haynes RB, Clark WF. Long-term renal prognosis of diarrhea-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Jama. 2003;290:1360–70. doi: 10.1001/jama.290.10.1360. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

