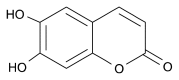
Analysis and distribution of esculetin in plasma and tissues of rats after oral administration
- PMID: 25580397
- PMCID: PMC4287325
- DOI: 10.3746/pnf.2014.19.4.321
Analysis and distribution of esculetin in plasma and tissues of rats after oral administration
Abstract
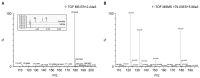
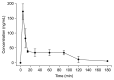
In this study, we developed a method to quantify esculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin) in plasma and tissues using HPLC coupled with ultraviolet detection and measured the level of esculetin in rat plasma after oral administration. The calibration curve for esculetin was linear in the range of 4.8 ng/mL to 476.2 ng/mL, with a correlation coefficient (r(2)) of 0.996, a limit of detection value of 33.2 ng/mL, and a limit of quantification value of 100.6 ng/mL. Recovery rates for the 95.2 ng/mL and 190.5 ng/mL samples were 95.2% and 100.3%, within-runs and 104.8% and 101.0% between-runs, respectively. The relative standard deviation was less than 7% for both runs. In the pharmacokinetic analysis, the peak plasma esculetin level was reached 5 min after administration (Cmax=173.3 ng/mL; T1/2=45 min; AUC0 ~180 min=5,167.5 ng · min/mL). At 180 min post-administration (i.e., after euthanasia), esculetin was only detectable in the liver (30.87±11.33 ng/g) and the kidney (20.29±7.02 ng/g).
Keywords: HPLC; esculetin; pharmacokinetics; plasma.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou L, Kang J, Fan L, Ma XC, Zhao HY, Han J, Wang BR, Guo DA. Simultaneous analysis of coumarins and secoiridoids in Cortex Fraxini by high-performance liquid chromatography–diode array detection–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008;47:39–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2007.12.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Okada Y, Miyauchi N, Suzuki K, Kobayashi T, Tsutsui C, Mayuzumi K, Nishibe S, Okuyama T. Search for naturally occurring substances to prevent the complications of diabetes. II. Inhibitory effect of coumarin and flavonoid derivatives on bovine lens aldose reductase and rabbit platelet aggregation. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1995;43:1385–1387. doi: 10.1248/cpb.43.1385. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources